 |
|
 |
 |
牙科知識人人須知(591)智齿与偏头痛
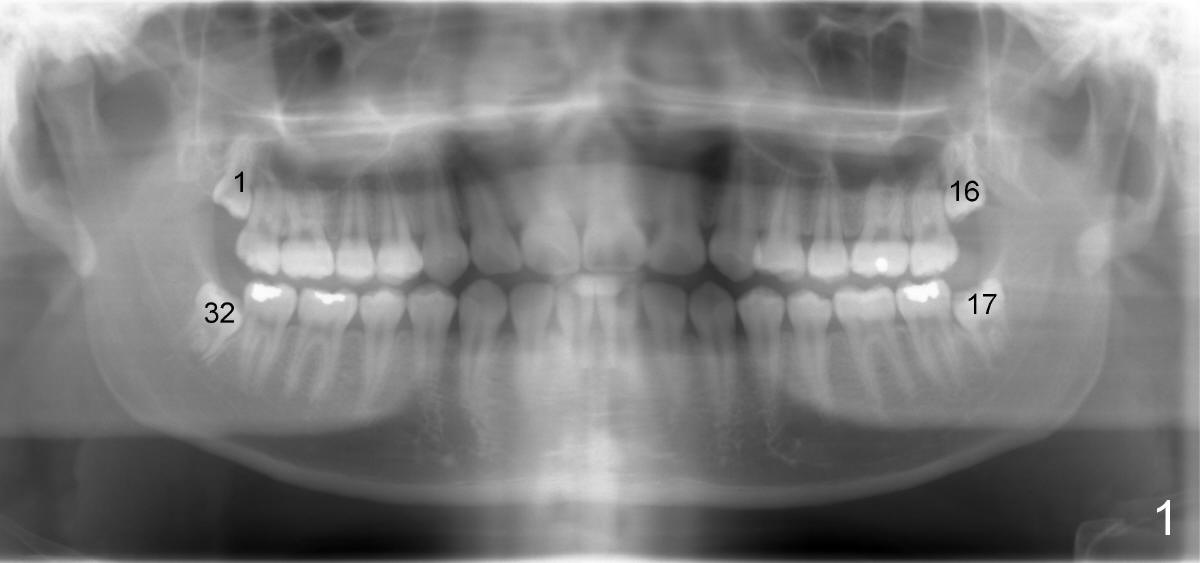
十六岁Alex长的特别快,三个月前妈妈带他来诊所会诊,他有严重右边偏头痛,妈妈问是不是与智齿阻生有关,吃偏头痛药很贵,多吃药对身体也不好。当妈妈年轻时,也有偏头痛,智齿拔除后,偏头痛便没有了。拍摄全景X光片,显示他的确有四个阻生智齿(图一:1,16,17,32)。三十二号牙长的特别歪(右下),母子俩决心大,同意一口气拔除两个智齿(1 (右上),32(右下)。
一晃三个月过去了,寒假到了,妈妈又带着Alex来诊所洗牙复诊,拔牙窝已经长好了,更重要的是偏头痛已经是过去式了。这是为什么呢?
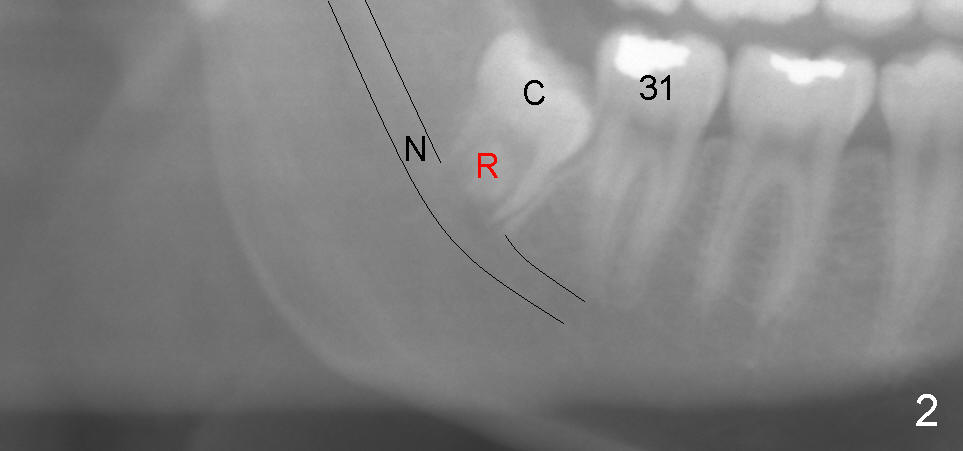
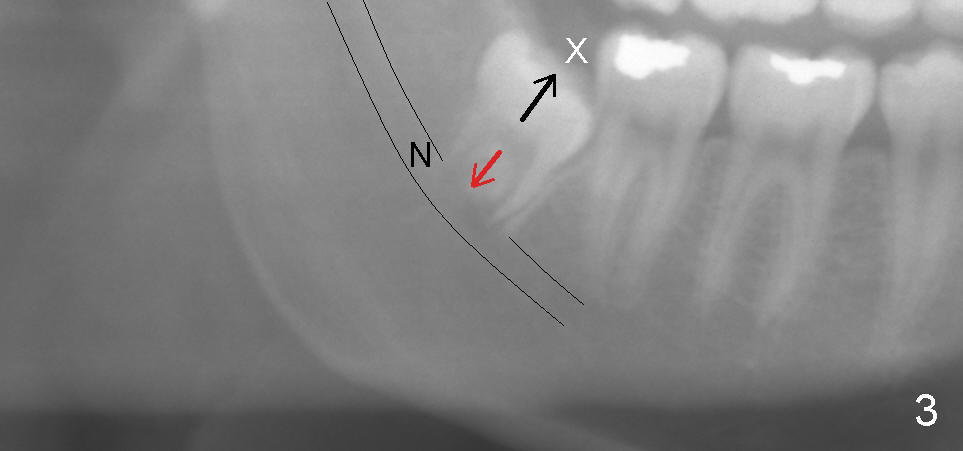
图二,图三是图一在三十二号牙(右下智齿)放大,它们显示智齿牙冠(图二:C)被它的邻牙(三十一号牙)阻挡了(图三x),长不出口腔(黑箭头),拼命要长高的智齿只能搞地下工作:它的牙根(图二:R)往下面神经管伸长发展,压迫里面的神经(图二图三:N)。这个在下颌骨当中的神经称为下牙槽神经,它是三叉神经(第五对颅神经)第三支中一个分支,三叉神经第三支中另外一个分支叫做中脑膜神经,支配脑膜感觉。三叉神经有个特点:分支之间互相通电话。有时前牙发炎时,同一侧后牙却痛起来,让病人捉摸不定。同一个道理:一侧下牙槽神经受压迫,疼痛却反射到同一侧大脑里。一旦智齿拔除,牙床没有压迫,偏头痛便不翼而飞。
魏心牙科博士初稿12/23/2012,最后一次修改01/19/2018
Wisdom Teeth and Migraine
Sixteen-year-old was brought by his mother to our office for consultation 3 months ago. Their concern is that Alex has migraine on the right side. It was treated by an expensive medicine. The mother wondered whether migraine is related to wisdom tooth impaction. When the mother was his age, she also had migraine, which was gone when wisdom teeth were removed.
We took -ray for Alex. It shows that he has indeed 4 wisdom teeth: # in Fig.1. The two right wisdom teeth were removed (#1,32). Yesterday Alex returned for cleaning and exam. The wounds heal completely. Surprisingly, his migraine is gone. How?
Fig.2,3 are a magnification of Fig.1 around the tooth #32, the lower right wisdom tooth. They show that the crown () of the wisdom tooth is blocked () by the neighboring tooth, #31, whereas the root (R) of the wisdom tooth is immediately next to the nerve (N) underneath. When the root grows long, the tooth (crown) is growing into the mouth (Fig.3: black arrow) while the root remains in the same place. When the tooth is impacted, i.e., blocked by a neighboring tooth (x), the elongating root grows toward the nerve (red arrow). Therefore, the nerve gets pinched more and more. This nerve inside the lower jaw (inferior alveolar nerve) is a branch of the third division of the trigeminal nerve (#5 cranial nerve). Another branch of the third division of the trigeminal nerve is called the middle meningeal nerve, which goes into our brain. Any branch of a nerve is related to the other. When the inferior alveolar nerve is pinched by a growing root of the wisdom tooth, the damage and resulting pain is reflected to the other branch, i.e., the middle meningeal nerve, causing migraine. When the wisdom tooth is extracted, there is no more pinch upon the nerve inside the lower jaw, no more reflecting pain or migraine.
Xin Wei, DDS, PhD, MS 1st edition 12/22/2012, last revision 01/19/2018