 |
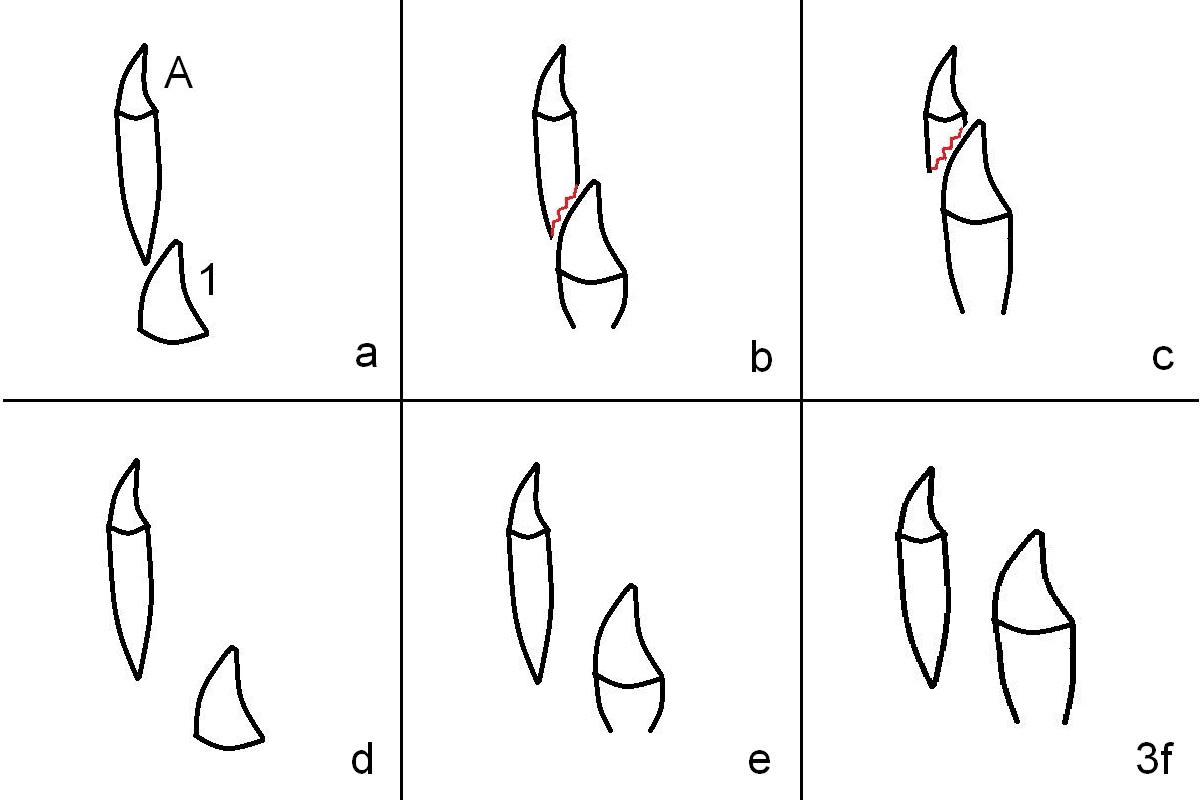
Fig.3 is cross section of development of baby (A) and adult (1) front teeth. Normally the former is more or less immediately above the latter (a). When the adult tooth starts to move up (b), the root of the baby tooth becomes resorbed and shortened (red saw-teethed). As the permanent tooth keeps growing, it eventually causes complete root resorption of the baby one (c).
In Elaine's case, the permanent tooth is too behind the baby one (d). When the former grows, it does not cause root resorption of its predecessor (e, f).
Xin Wei, DDS, PhD, MS 1st edition 07/17/2016, last revision 07/17/2016