 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
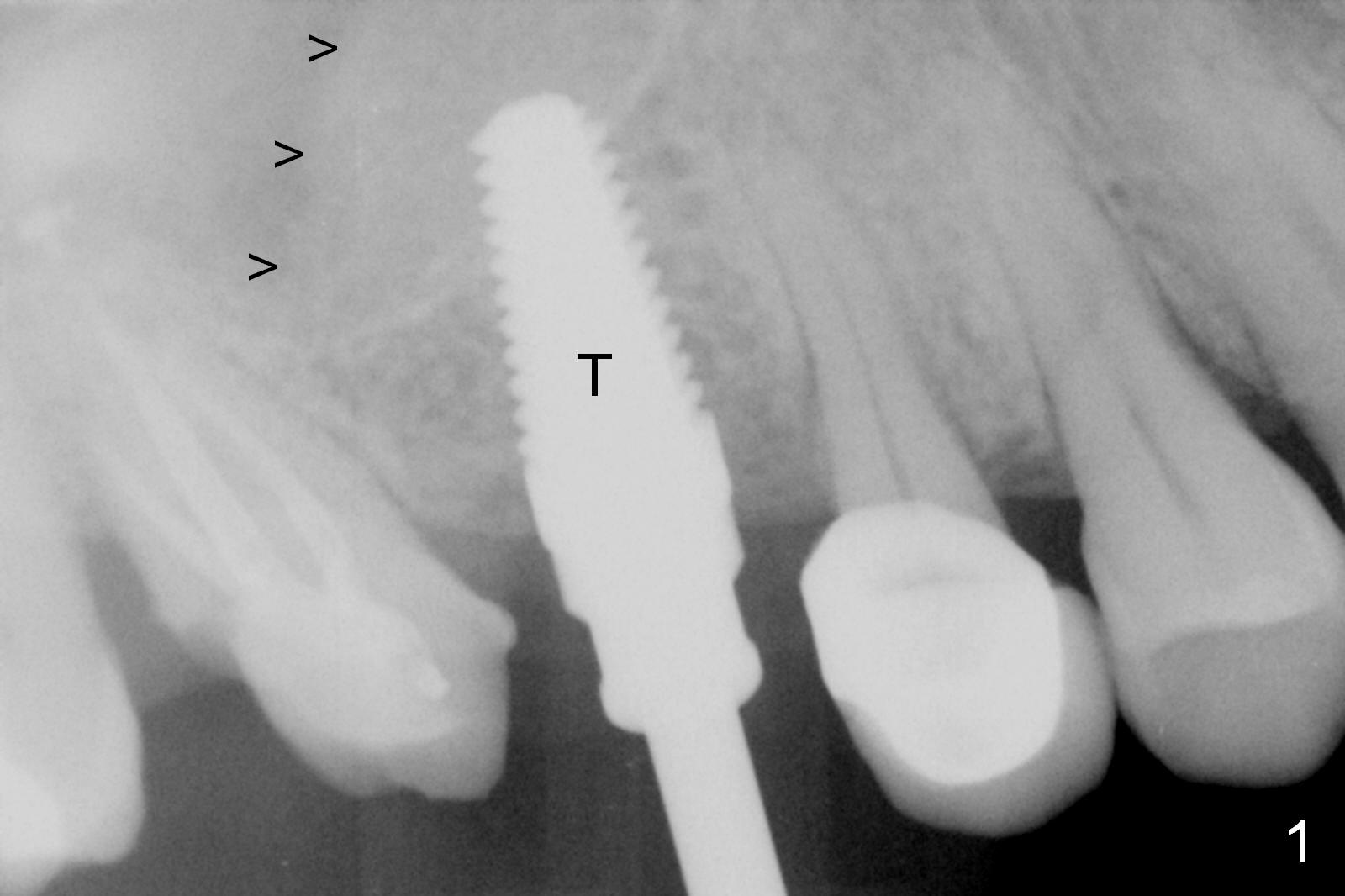
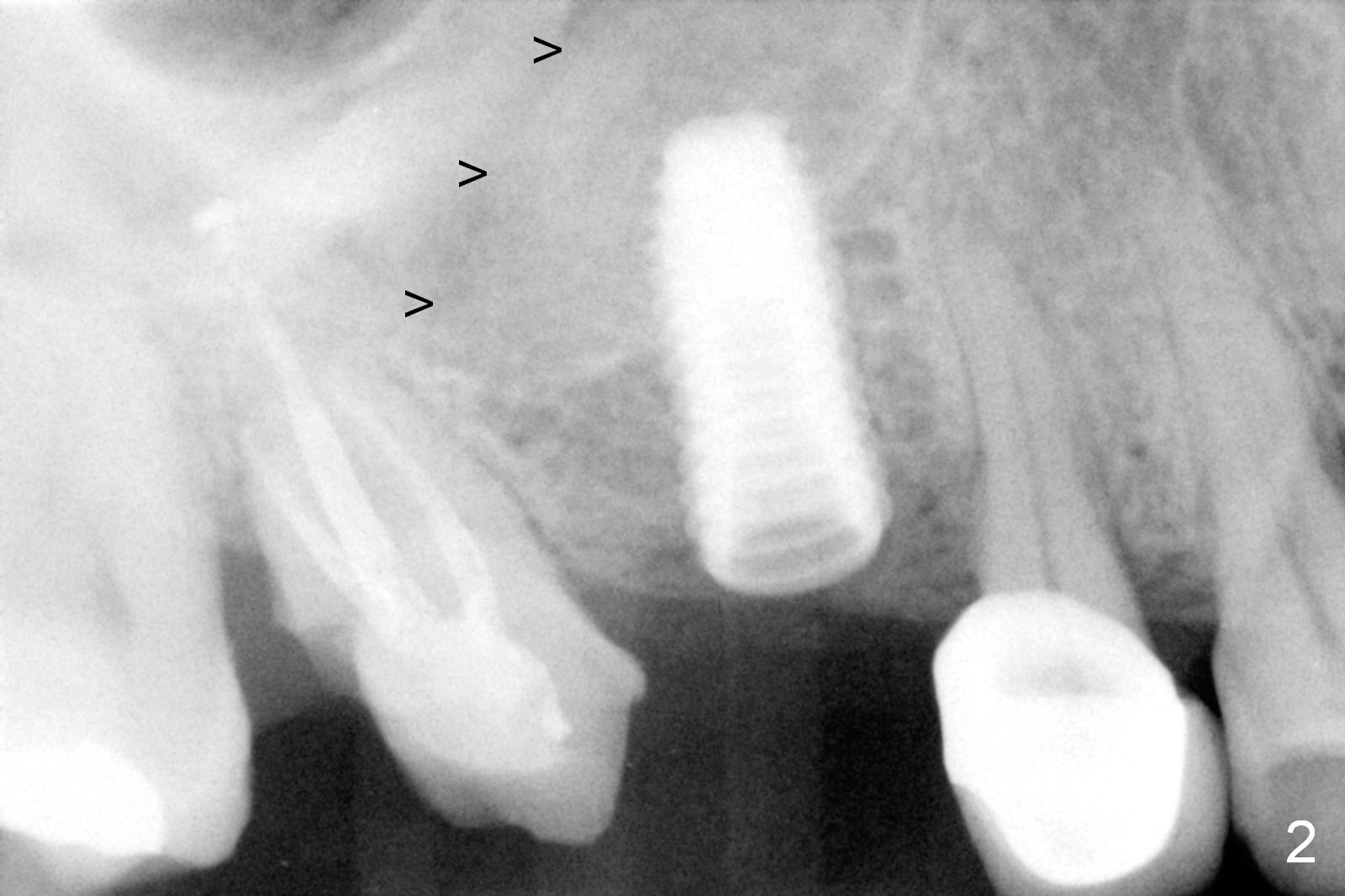
Bone Depth Control for Sinus Lift
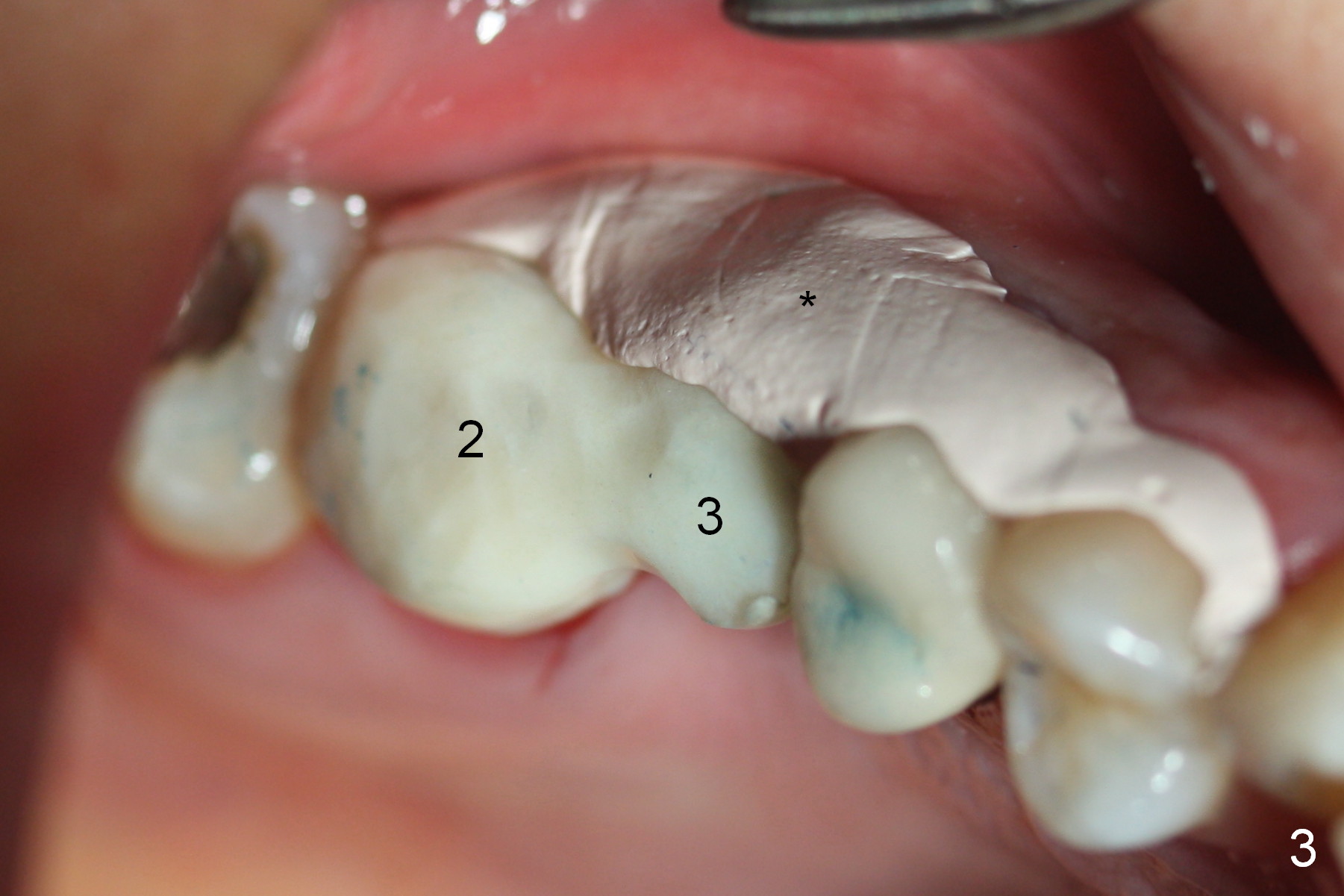
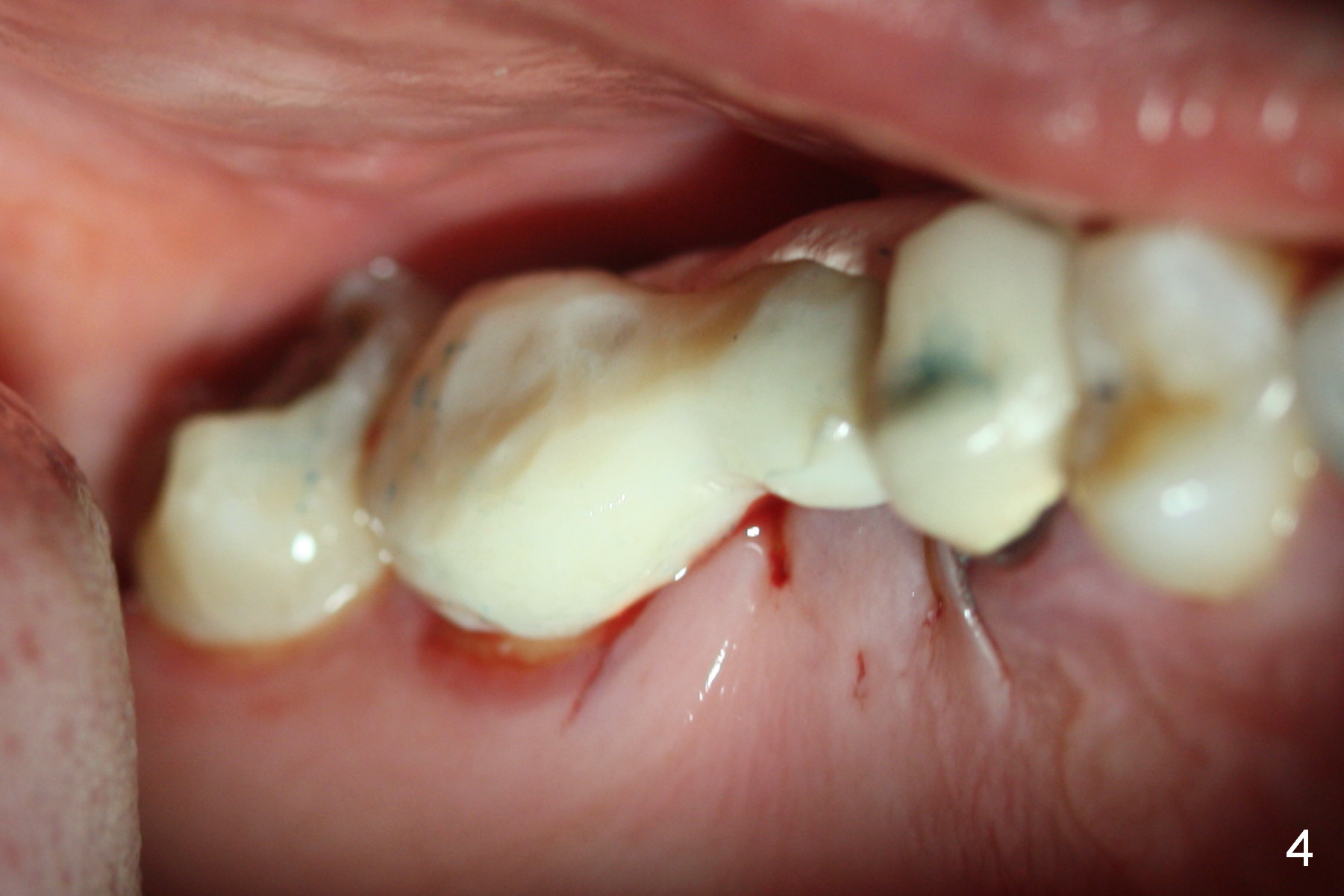
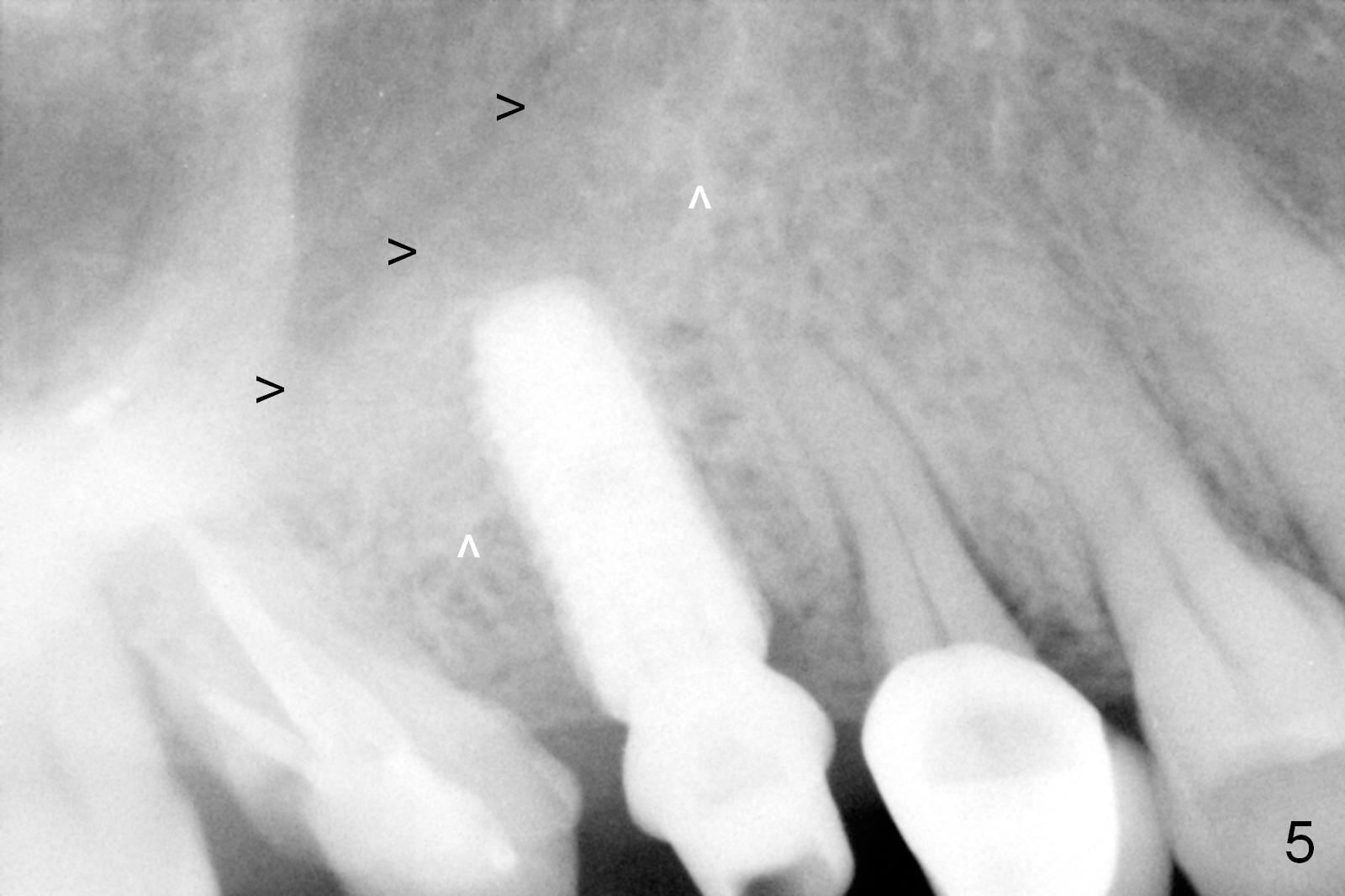
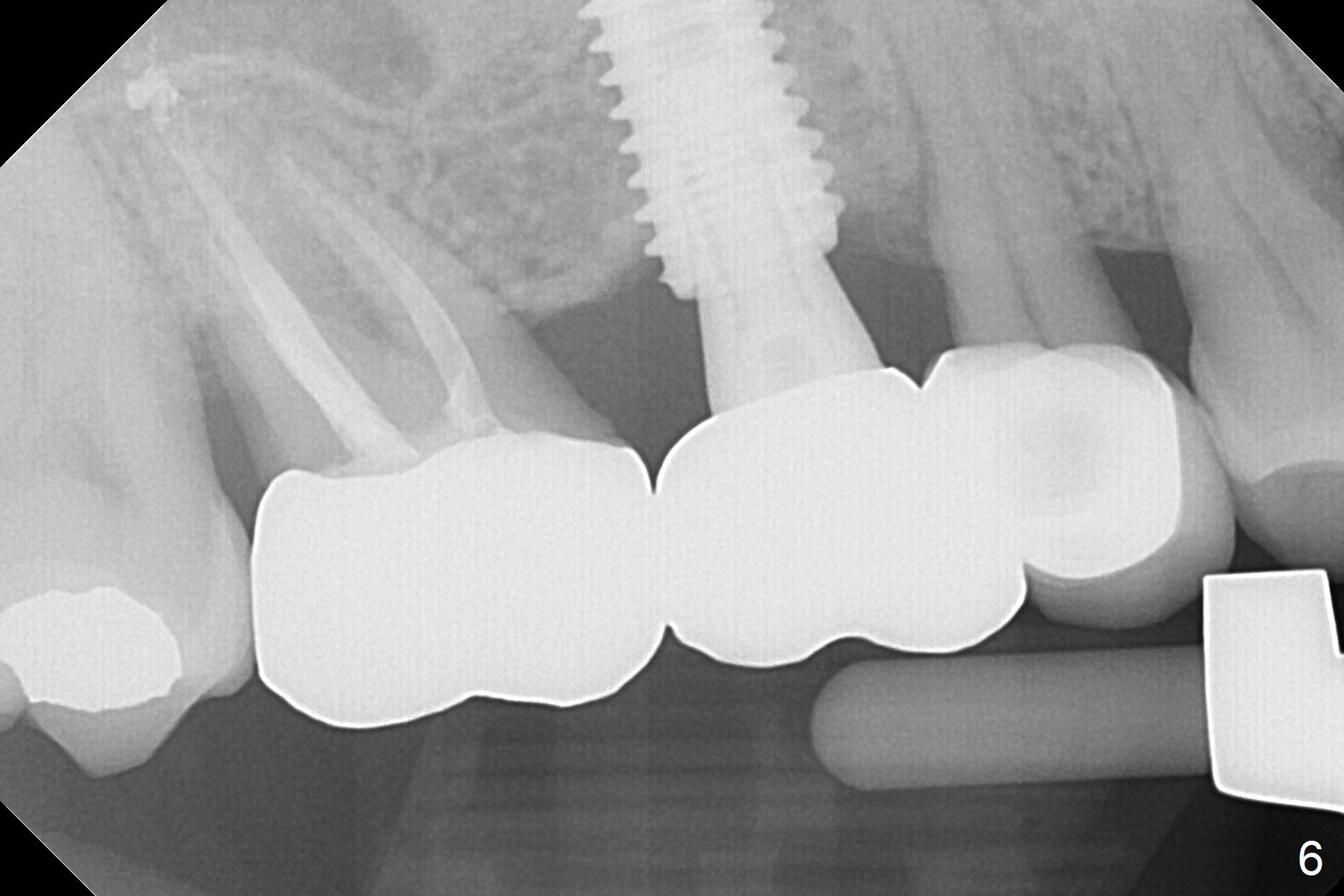
Bone expansion is carried out with #15 blade, 1 and 1.5 mm microosteotomes, RT 2,3, BS, BB prior to use of CAS kit with depth control. When a 5x14 mm tap is placed at the depth of 11 mm (Fig.1 T), bone graft is visible in the sinus (arrowheads). The phenomenon persists when a 5x11.5 mm UF implant is placed with insertion torque between 35 and 50 Ncm (Fig.2). An abutment is placed for fabrication of a splinted provisional at #2 and 3 (Fig.3). Approximation of the wound is not as perfect buccally as lingually (Fig.4) so that periodontal dressing is applied buccally (Fig.3 *). While the volume of the sinus lift reduces 4.5 months postop (Fig.5 black arrowheads), the sinus floor decreases in the density (white arrowheads, possibly due to loss of blood supply directly from the periosteum). There is no bone loss 15 months post cementation (Fig.6); the patient is pleased with the implant.
Return to Upper Molar Immediate Implant,
Posterior Immediate Provisional
Xin Wei, DDS, PhD, MS 1st edition 12/10/2015, last revision 09/02/2017