 |
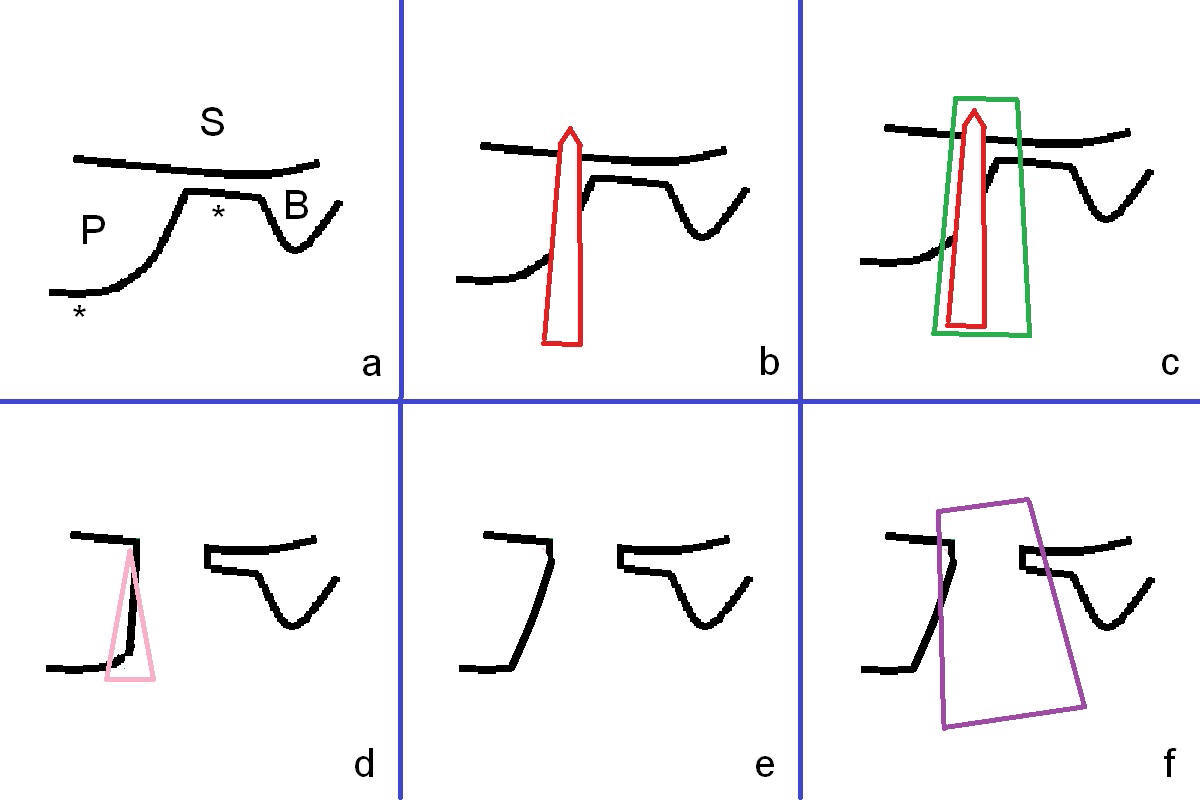
The tooth #2 is found to have fracture at extraction. The buccal (B) socket (*) has more resorption than the palatal (P) one (Fig. A (S: sinus). The buccal plate is also lower (B). Osteotomy is initiated in the buccal slope of the septum with Magic Expanders (ME, 3-4.8 mm, Fig. B (red)), followed by Tatum Tapered tap drills (Fig. C (green), Fig.1 (5x17 mm)). As the diameter of ME and tap increases, the osteotomy is shifting buccally due to bone height discrepancy (Fig. C). A Lindamann bur is used to remove the palatal bone (Fig. D (pink) and move the osteotomy palatally (Fig. E). The coronal end of 7x14 mm tissue-level fixture (Fig.2) tilts buccally (Fig. F purple). Insertion torque is 35/40 Ncm. Prior to implantation, a piece of PRF membrane and allograft are pushed into the sinus.
Xin Wei, DDS, PhD, MS 1st edition 01/31/2017, last revision 07/01/2018