 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Surgical Access to Impacted Canine
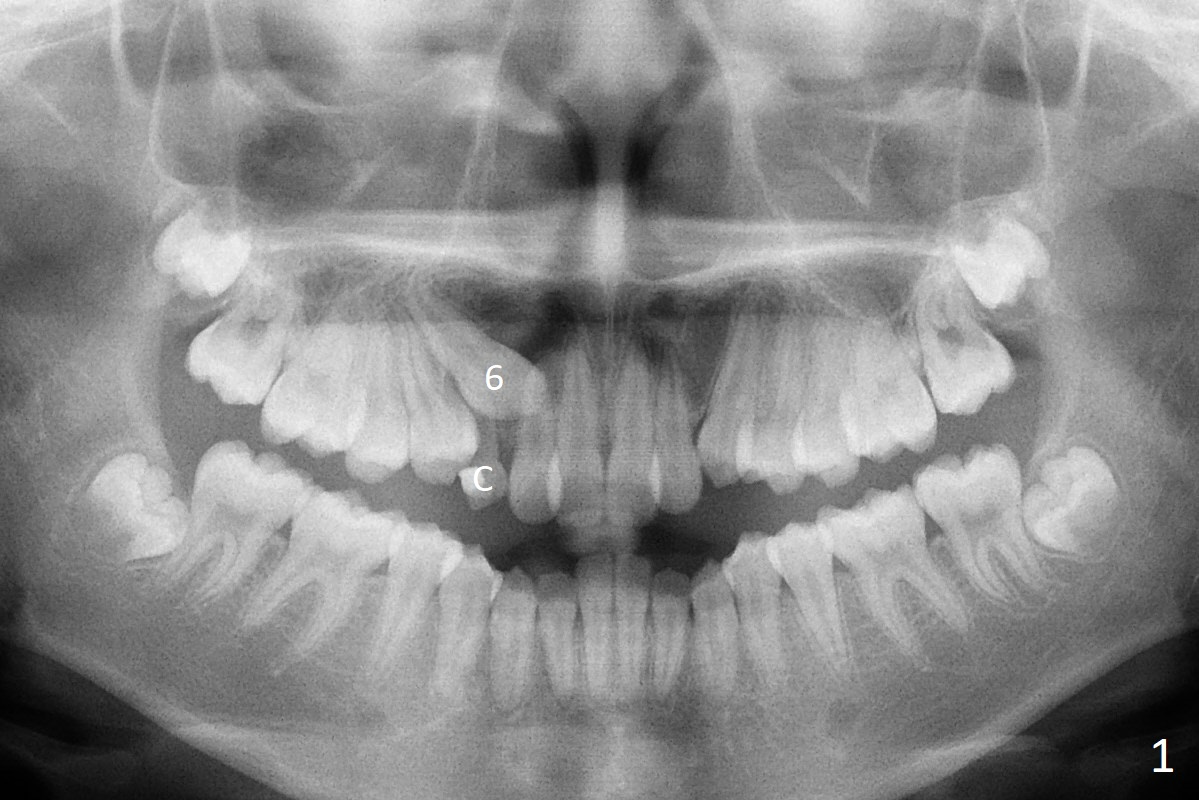
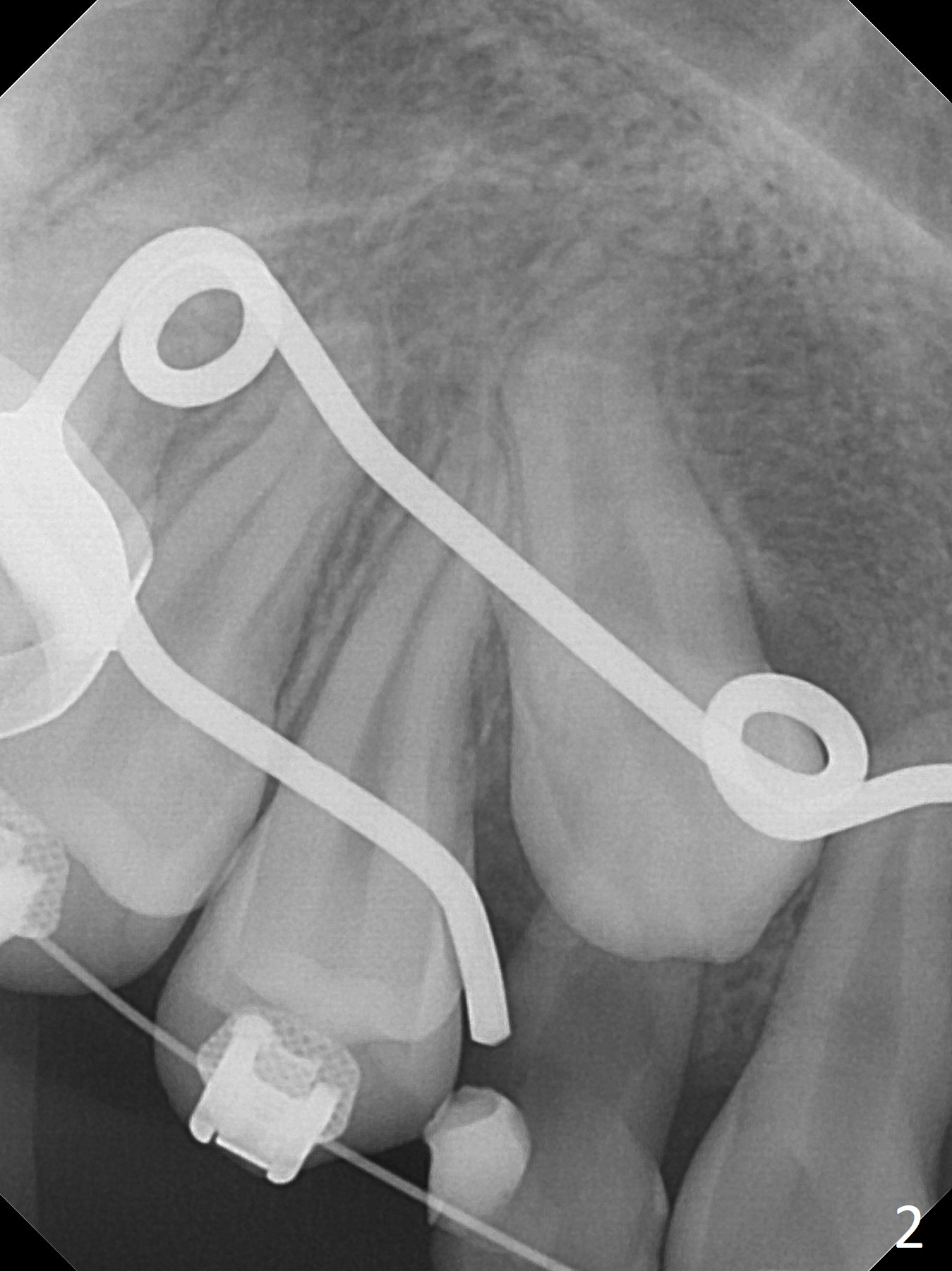
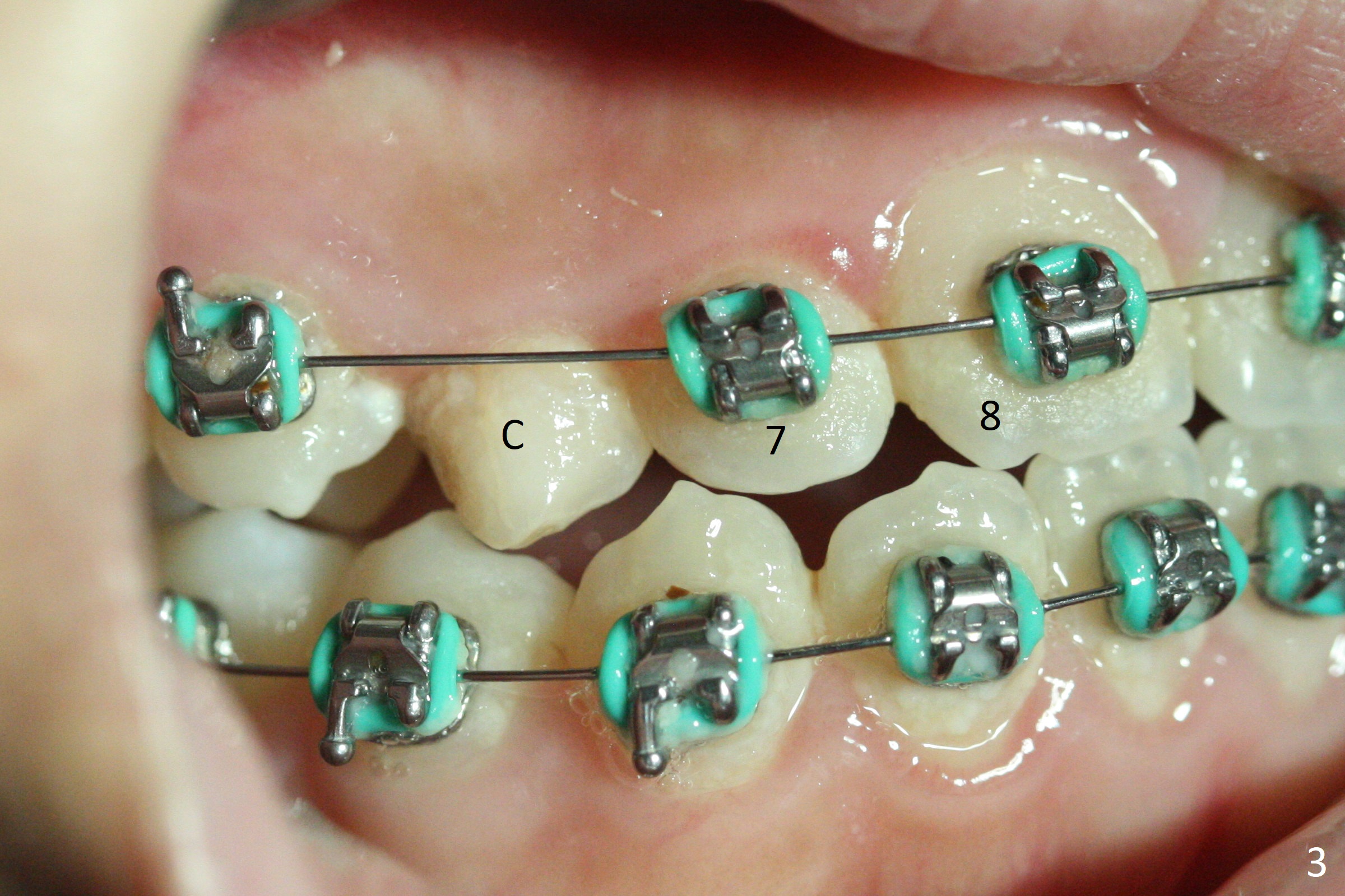
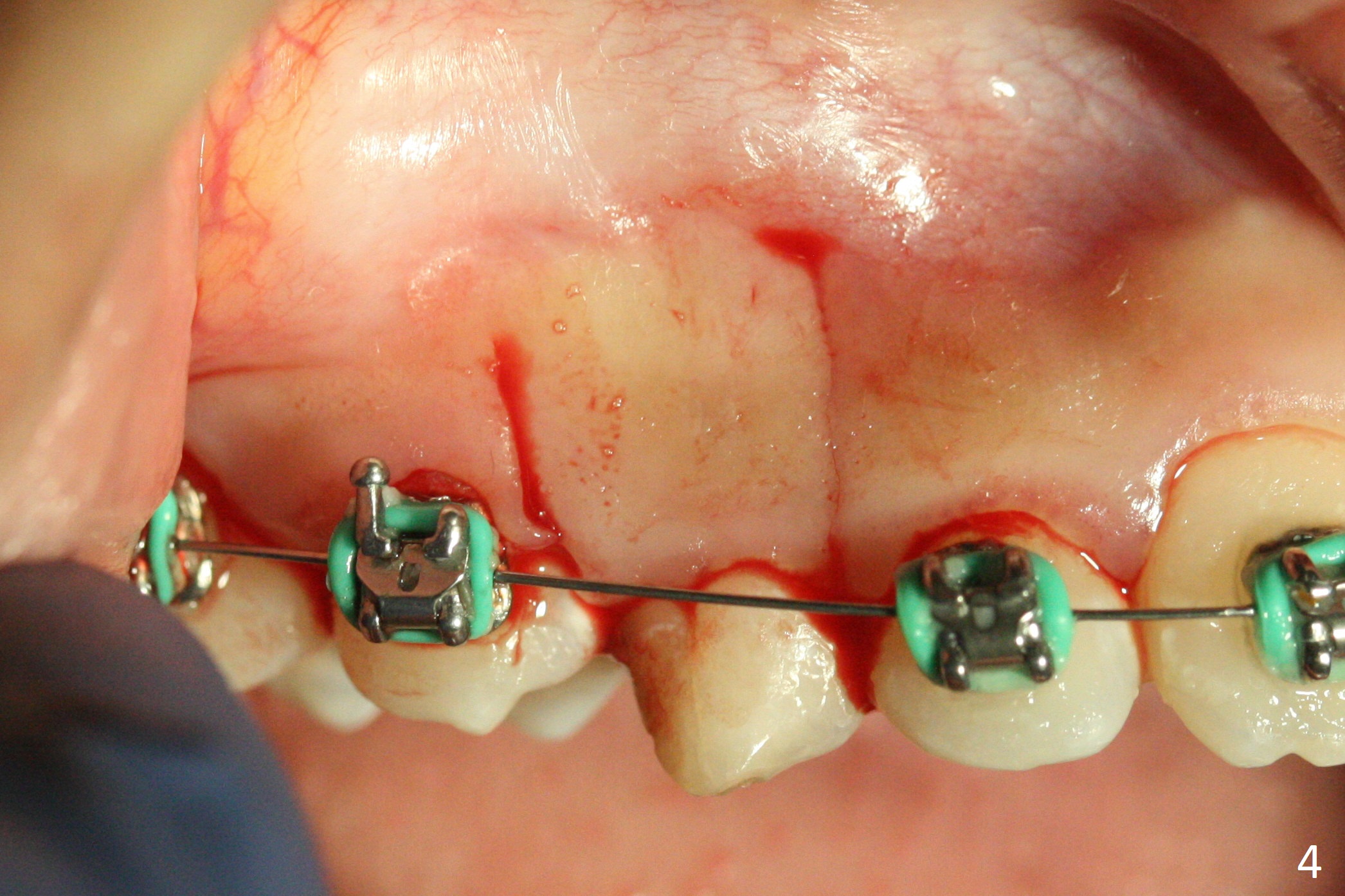
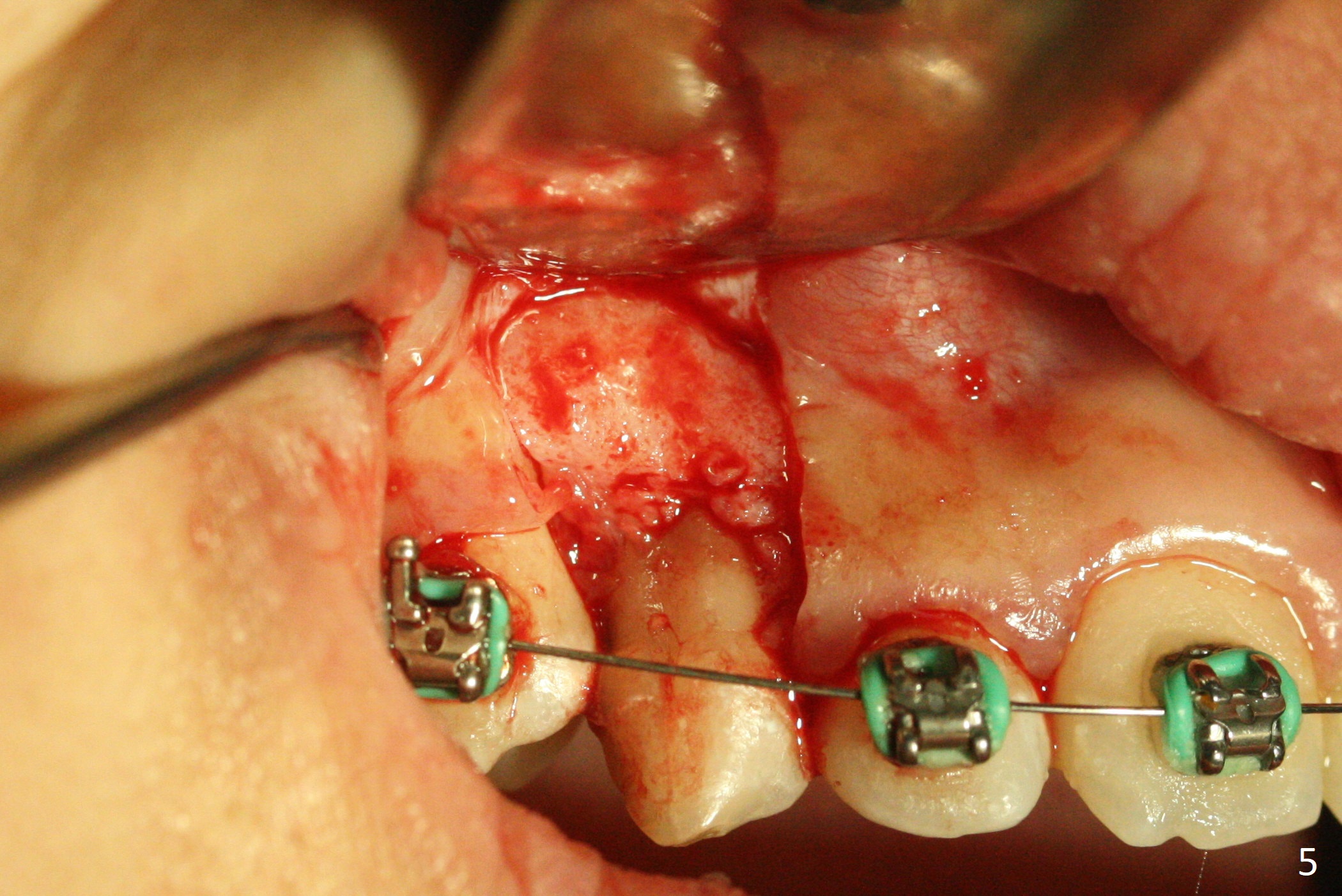
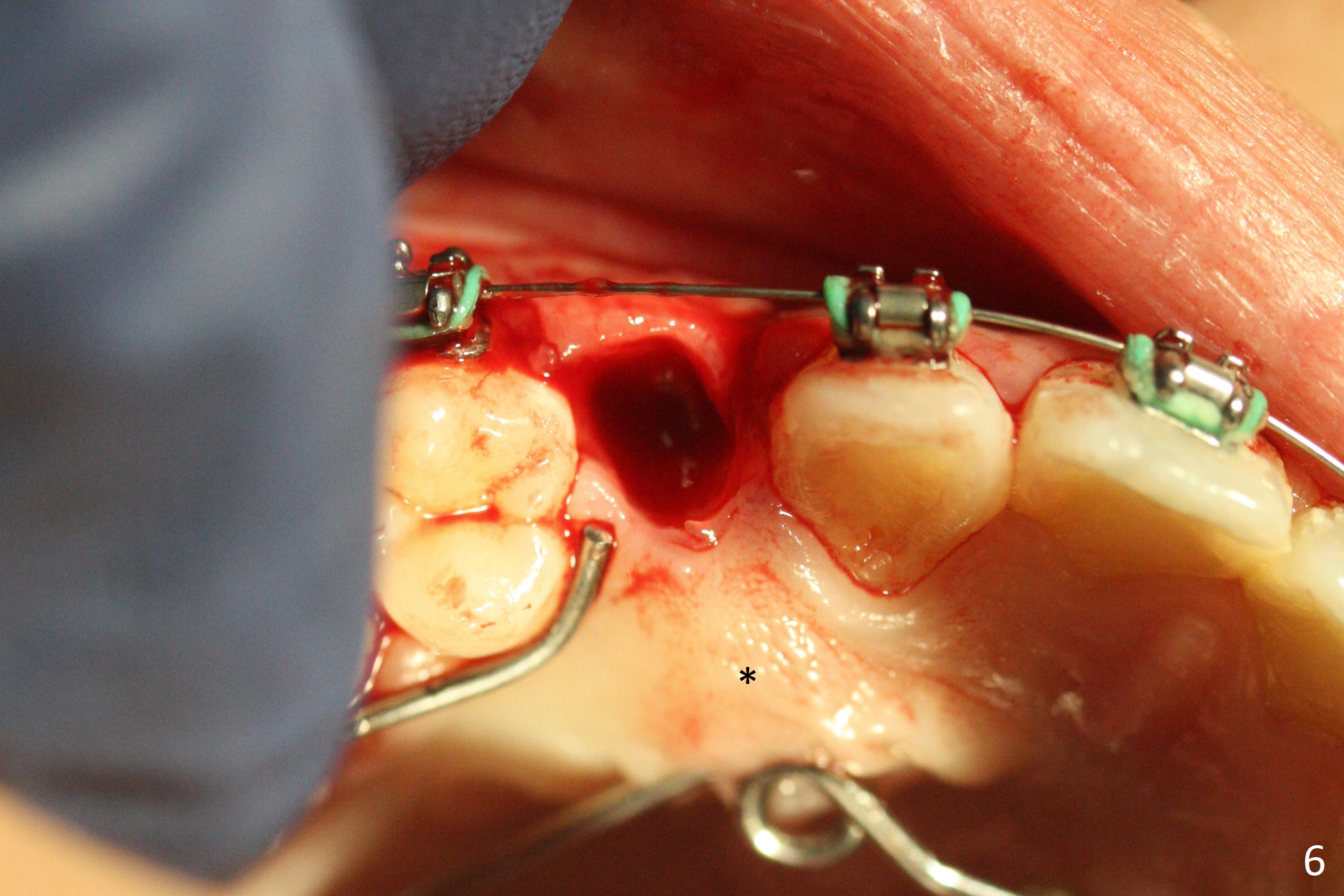
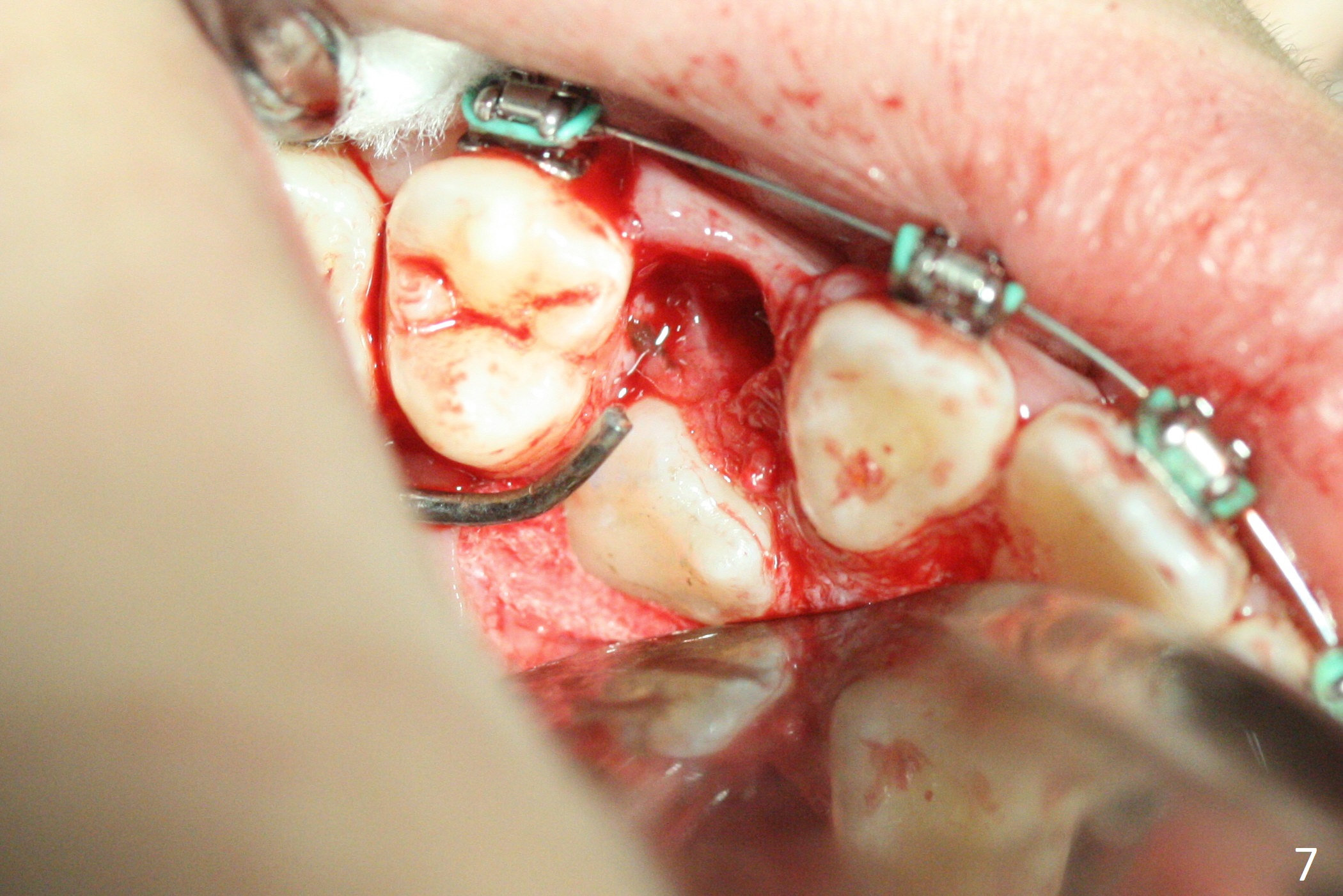
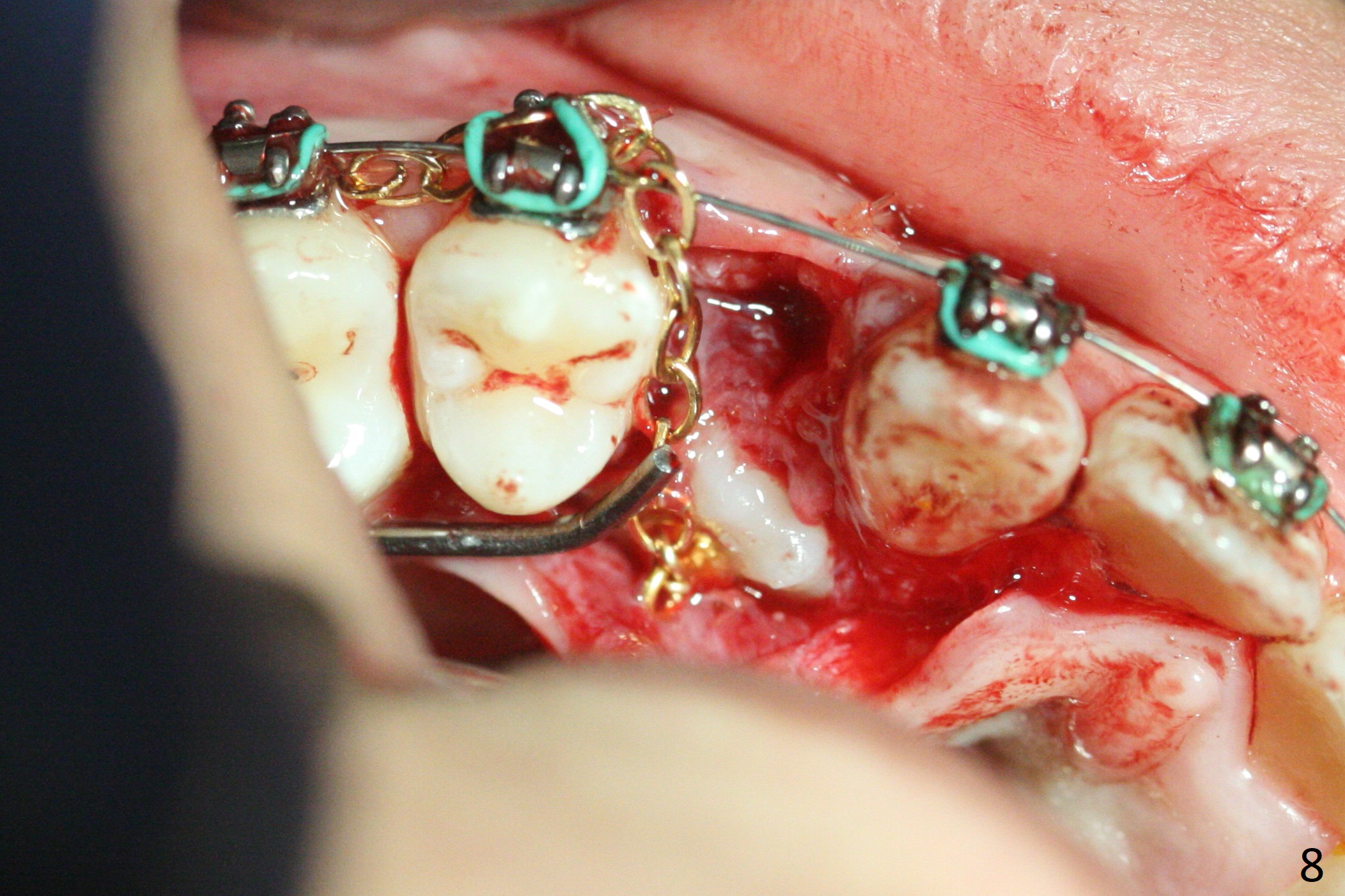
A 13-year-old woman has an impacted canine (Fig.1 (6)) and retained deciduous one (C). After initiation of orthodontics, she returns for surgical access to the impacted canine and placement of device to facilitate eruption (Fig.2,3). Incision is made buccal (Fig.4), but there is no tooth buccal (Fig.5). Extraction of the deciduous canine does not reveal the impacted one (Fig.6), but there is palatal elevation (*). Palatal access shows the impacted tooth (Fig.7) and allows placement of a retraction device (Fig.8). Careful clinical exam and CBCT are necessary diagnostic steps.
Return to Professionals Xin Wei, DDS, PhD, MS 1st edition 06/24/2019, last revision 06/24/2019