 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
CT, Better Planning
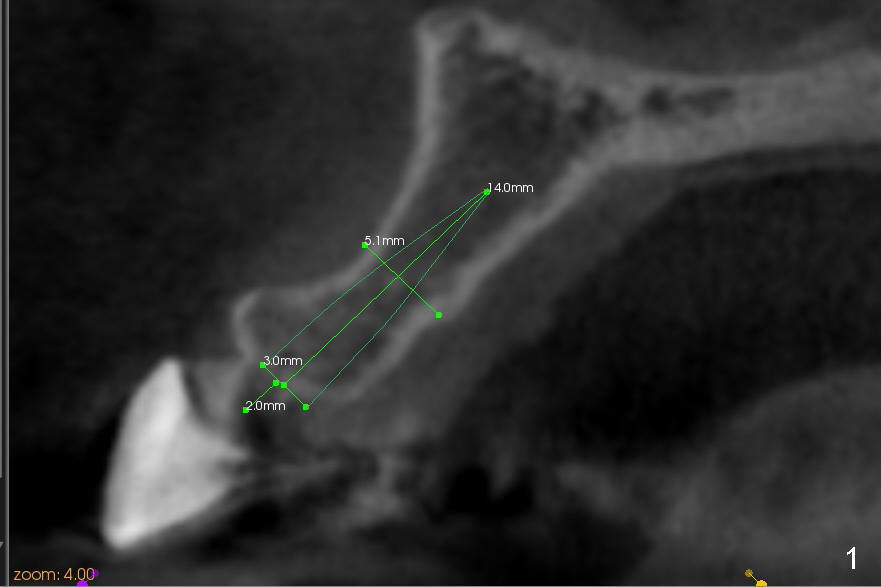
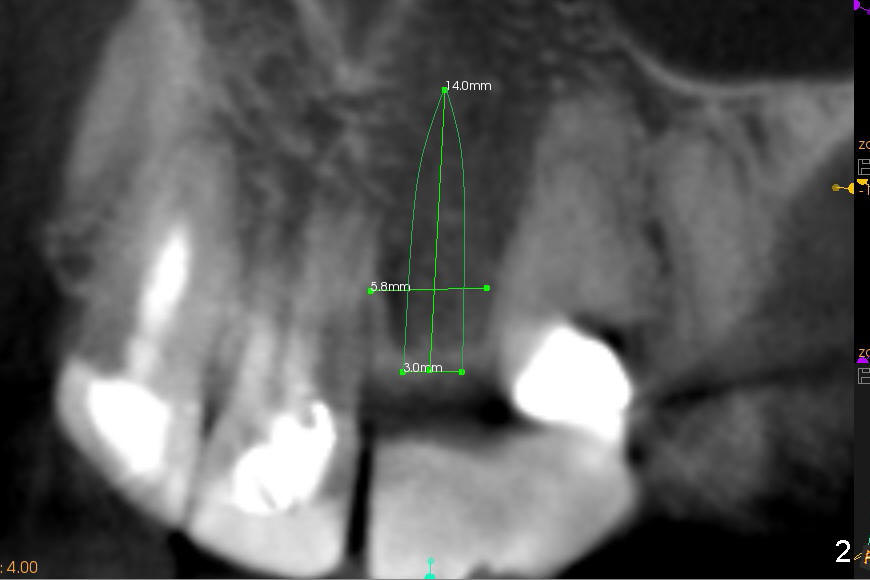
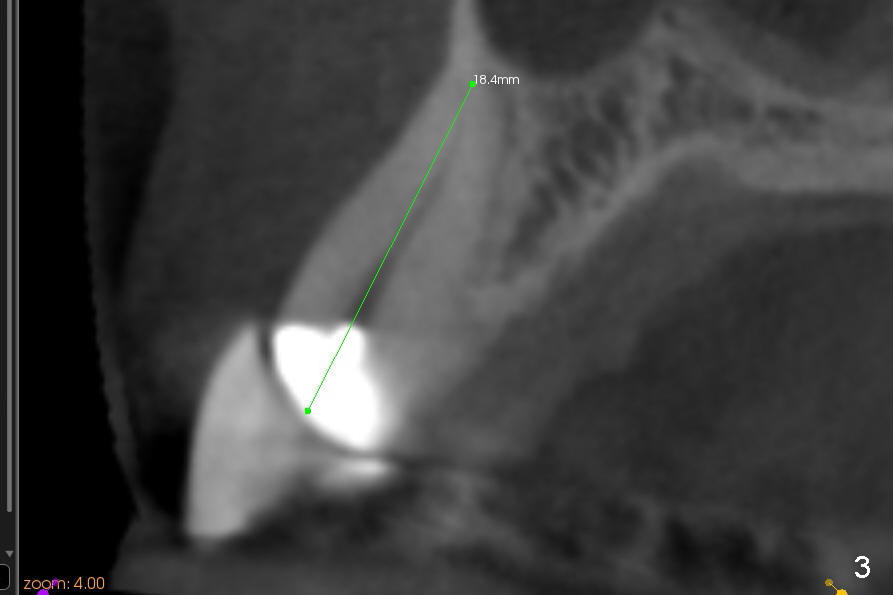
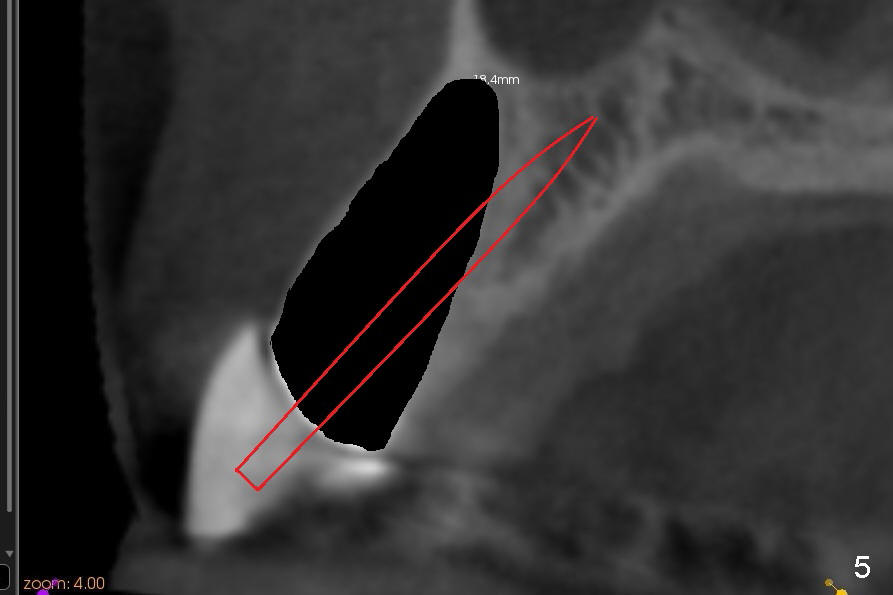
A 57-year-old lady used to have a bridge #9-11. Secondary subgingival caries of #11 makes it difficult to save the tooth (Fig.3 (CT coronal section)). She is wearing a provisional partial now. A 3x14 mm one piece implant appears to be appropriate at the site of #10 (Fig.1,2 (CT coronal and sagittal sections)).
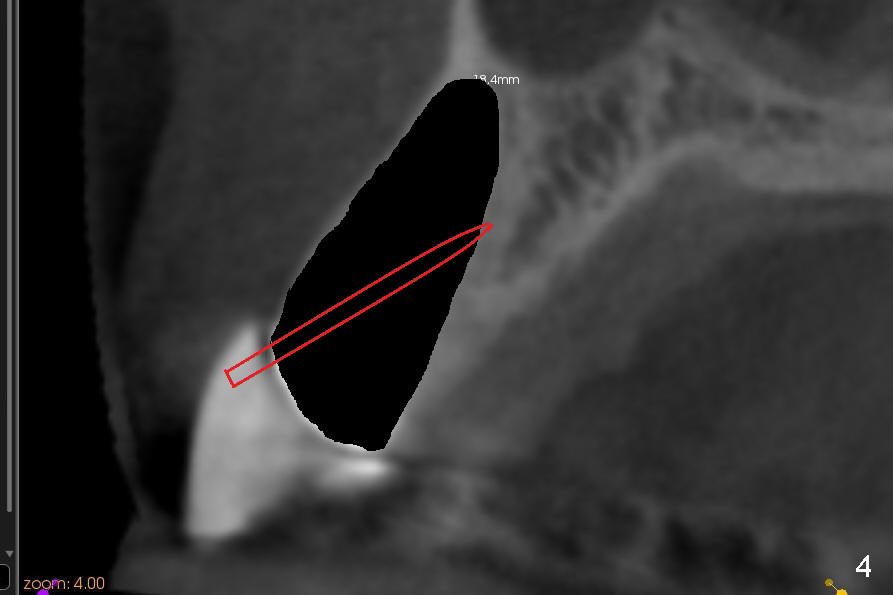
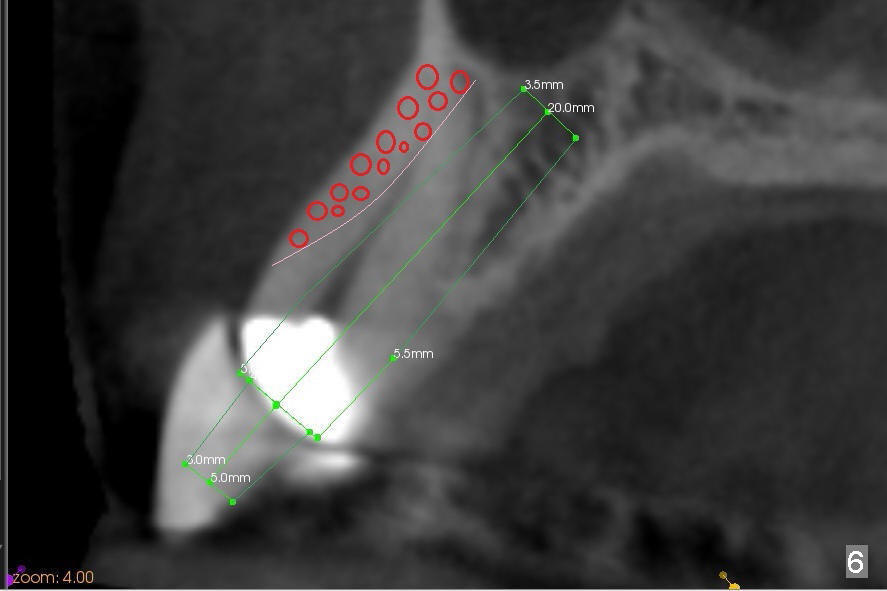
Immediate after extraction of the tooth #11 (Fig.4), a pilot drill is penetrating the palatal wall of the socket obliquely. Once the cortex of the palatal wall of the socket is penetrated, the trajectory changes so that the drill is more or less parallel to the palatal wall of the alveolus (Fig.5). Since the canine socket is large, particulate bone graft is placed in the buccoapical area of the socket (Fig.6 red circles) prior to implant placement. A curette is used to pack the graft against the labial wall and there is no blockage to the opening of the osteotomy. More bone graft is placed buccal and coronal to the implant once the latter is placed. CT images are helpful for treatment planning to reduce surgical complication. The benefits are multifold.
Return to Upper Canine Immediate Implant Atrophic Ridge Xin Wei, DDS, PhD, MS 1st edition 11/28/2014, last revision 02/03/2019