 |
 |
|
 |
||
7 mm Implant
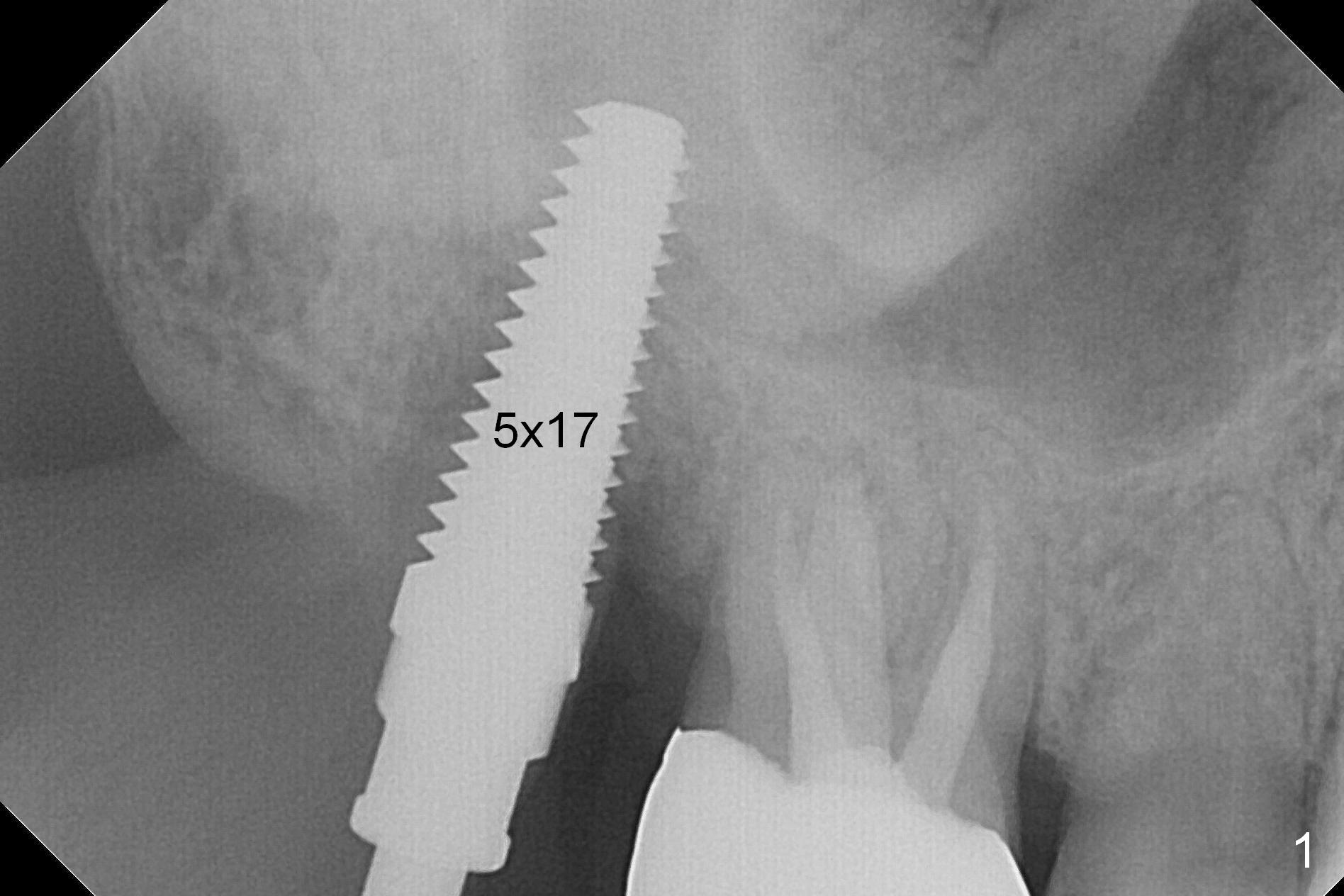
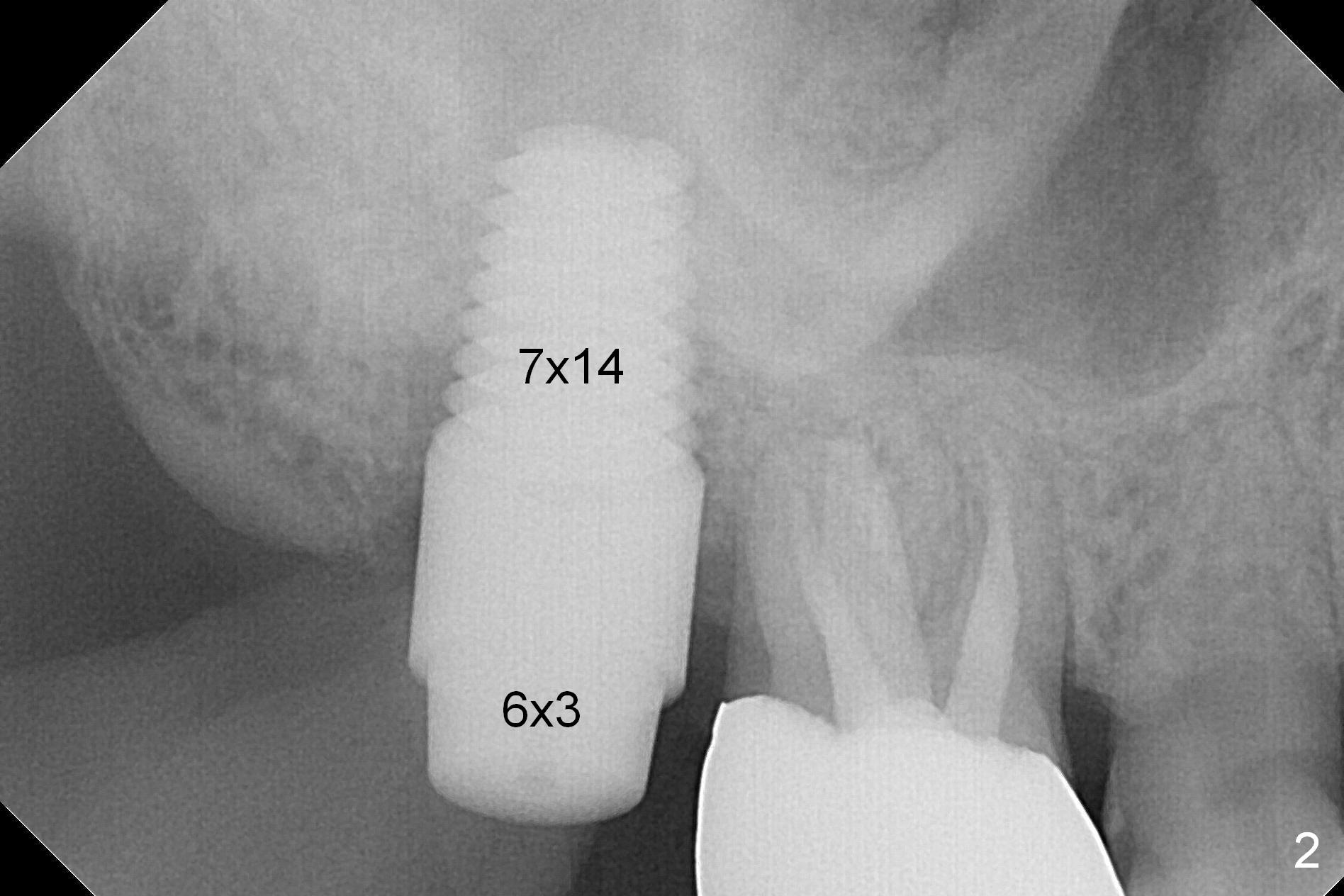
The tooth #2 is found fractured at extraction. The fused buccal (B) socket is deeper than the palatal (P) one (Fig. A * (S: sinus)); the buccal wall is low. The osteotomy is initiated in the buccal slope of the septum with Magic Expanders (3-4.8 mm, Fig. B (red)), followed by Tatum tapered tap drills (4.5-7 mm, Fig. C (green); Fig.1 (5 mm)). As the diameter of the tap drills increases, the osteotomy is shifting buccally, while larger taps are apparently losing stability. Lindamann bur is used to remove the palatal bone (Fig. D (pink) and move the osteotomy palatally (Fig. E). Because of bone height discrepancy, a 7x14 mm tissue-level implant tilts slightly buccally in the coronal end (Fig. F; Fig.2). Insertion torque is between 35 and 40 Ncm. A piece of PRF membrane and allograft is placed into the sinus prior to implantation. Following 6x3 mm abutment placement, more of allograft/Osteogen is placed in the remaining buccal and palatal sockets. A simplified provisional is applied around the implant/abutment for bone graft and collagen membrane retention.
Return to
Upper
Molar Immediate Implant, Prevent
Molar Periimplantitis (Protocols,
Table),
IBS
Xin Wei, DDS, PhD, MS 1st edition 01/31/2017, last revision 01/31/2017