 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
  |
 |
 |
Bone Expansion and Bending
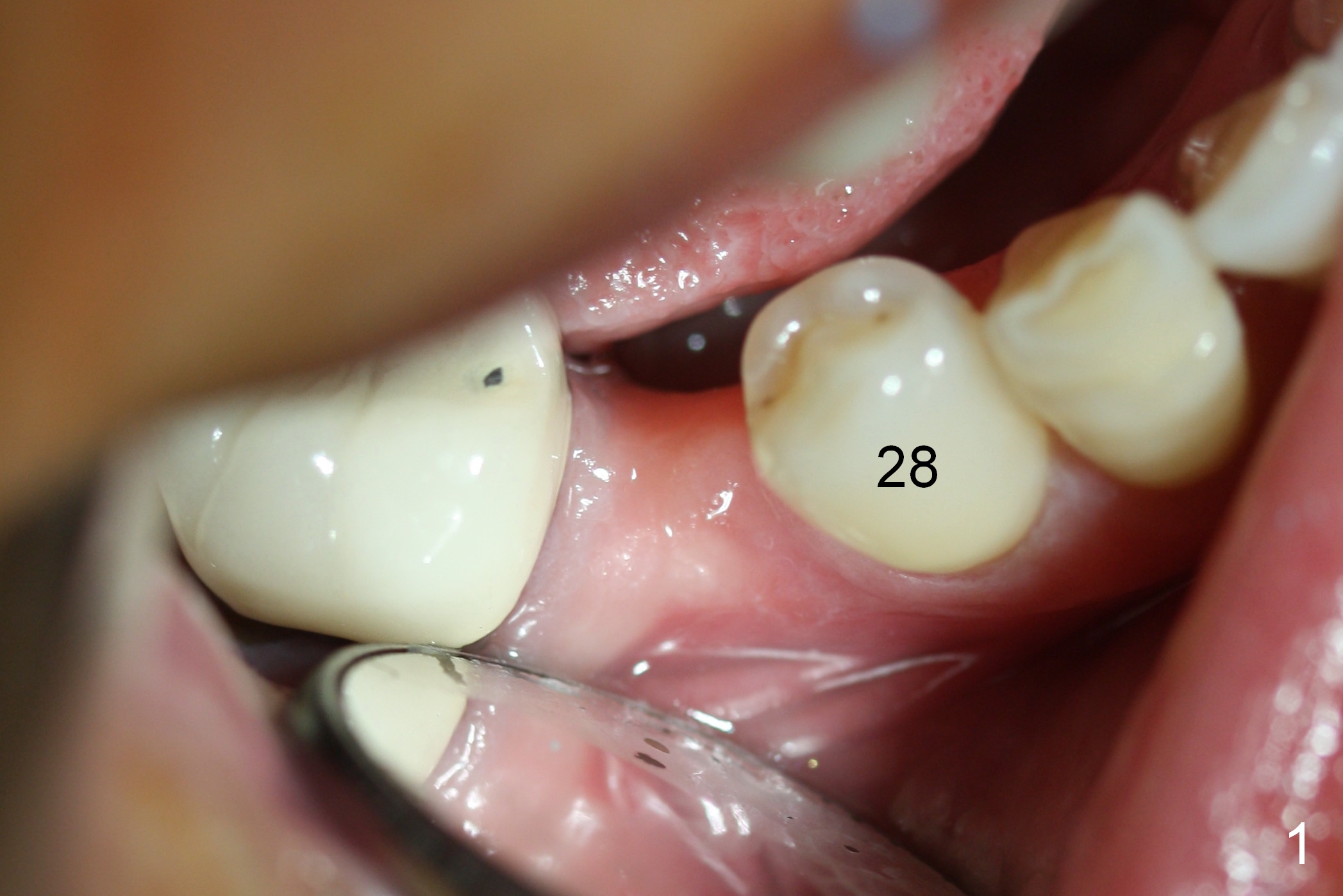
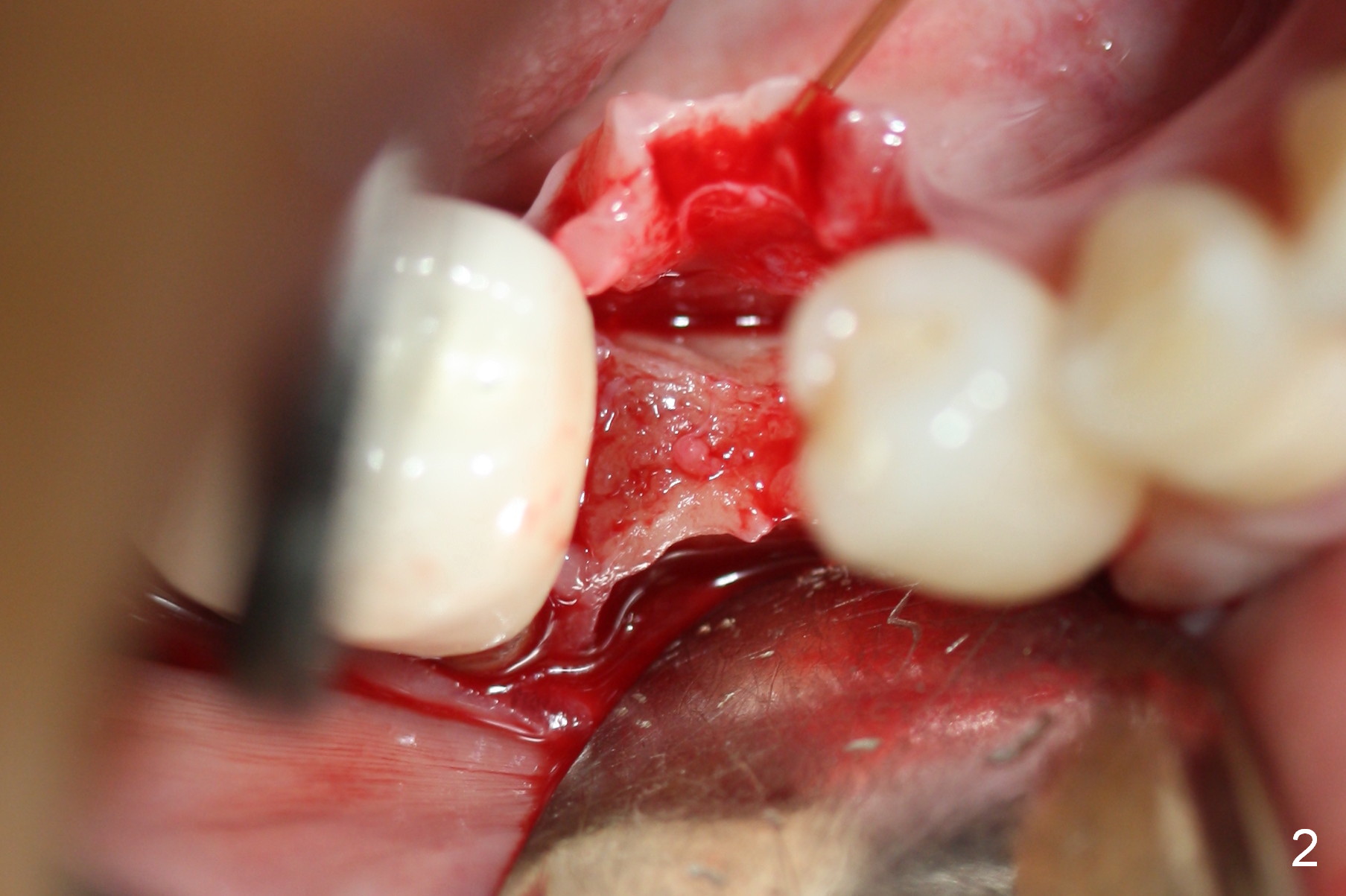
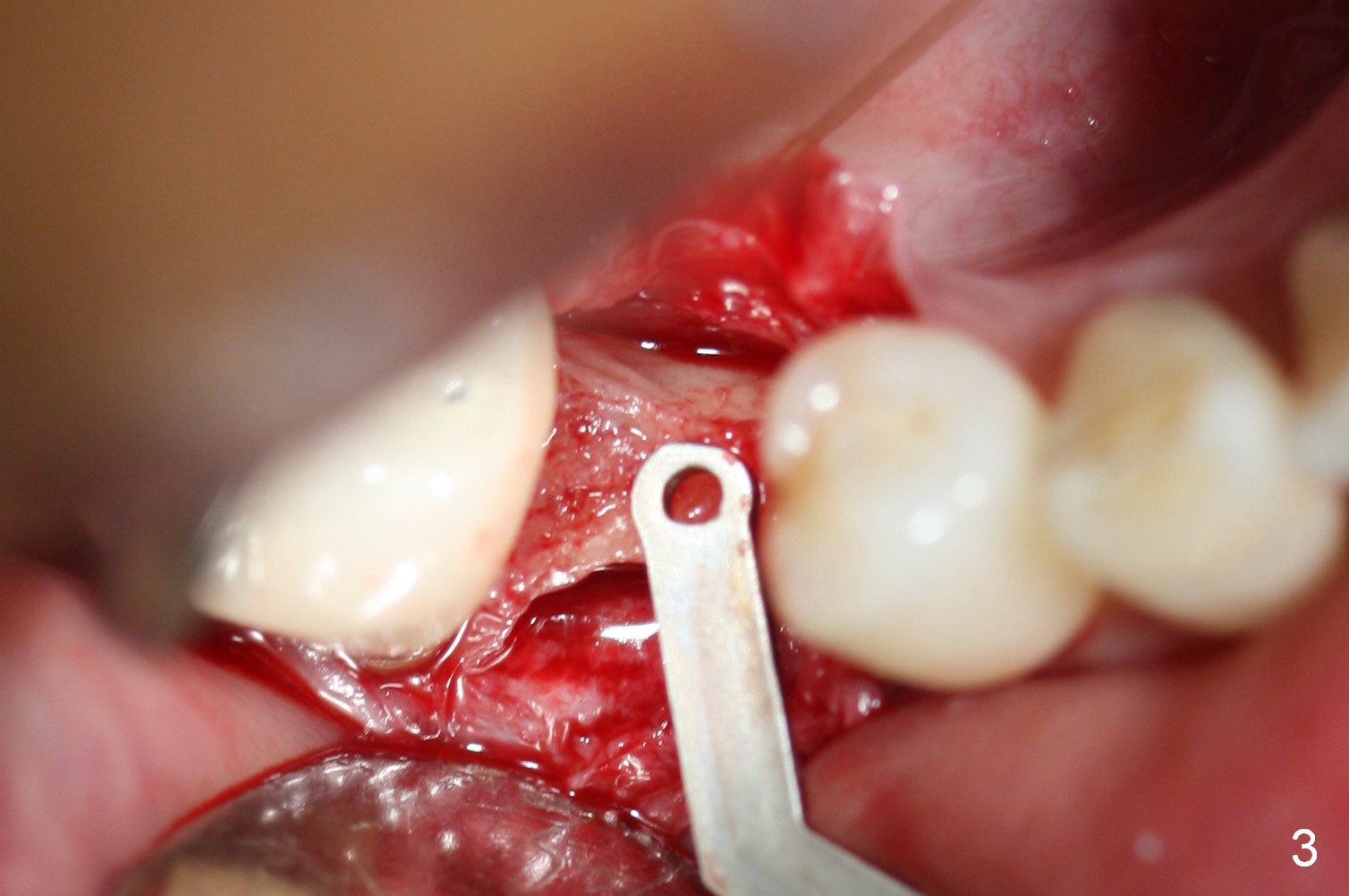
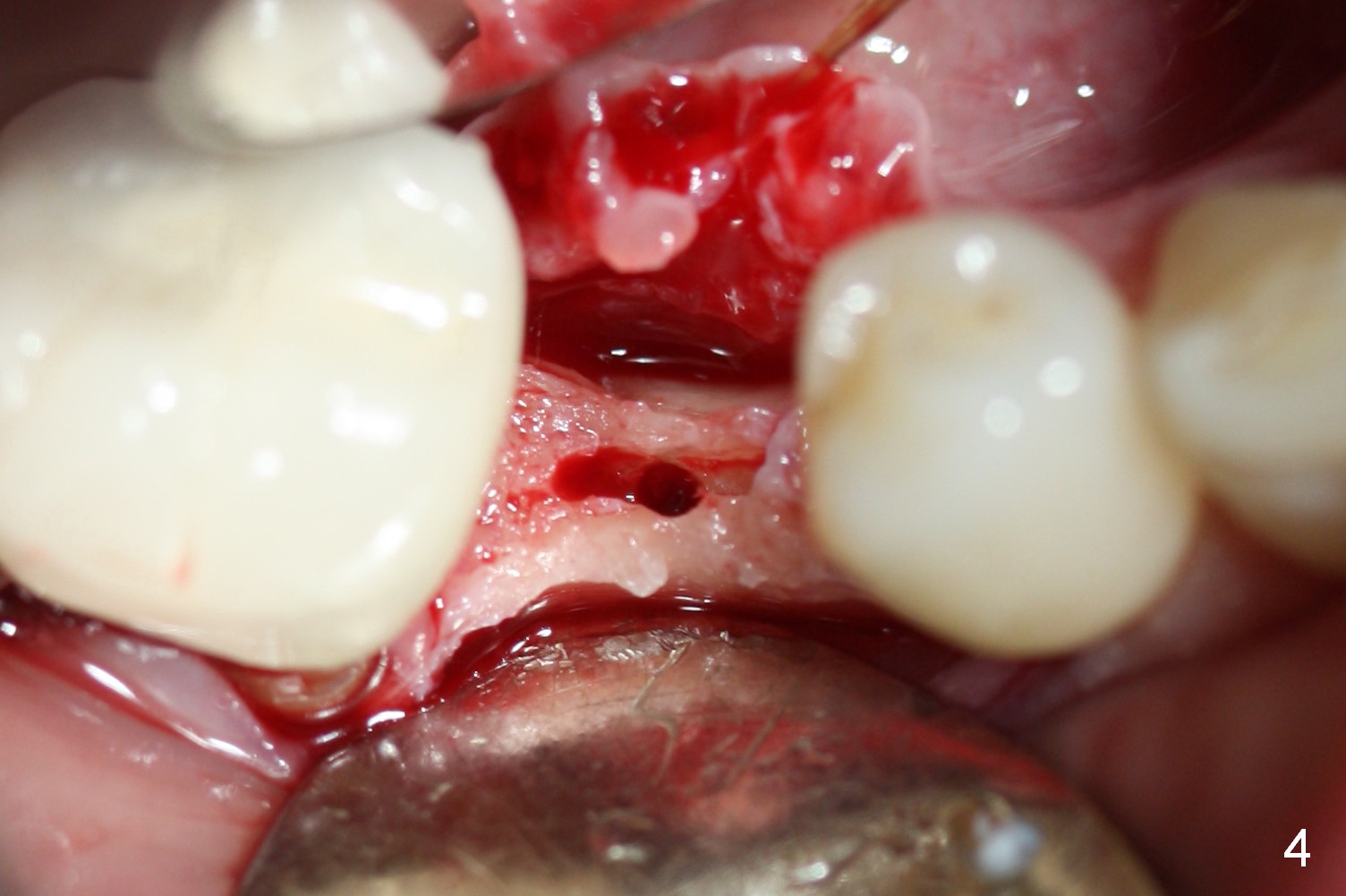
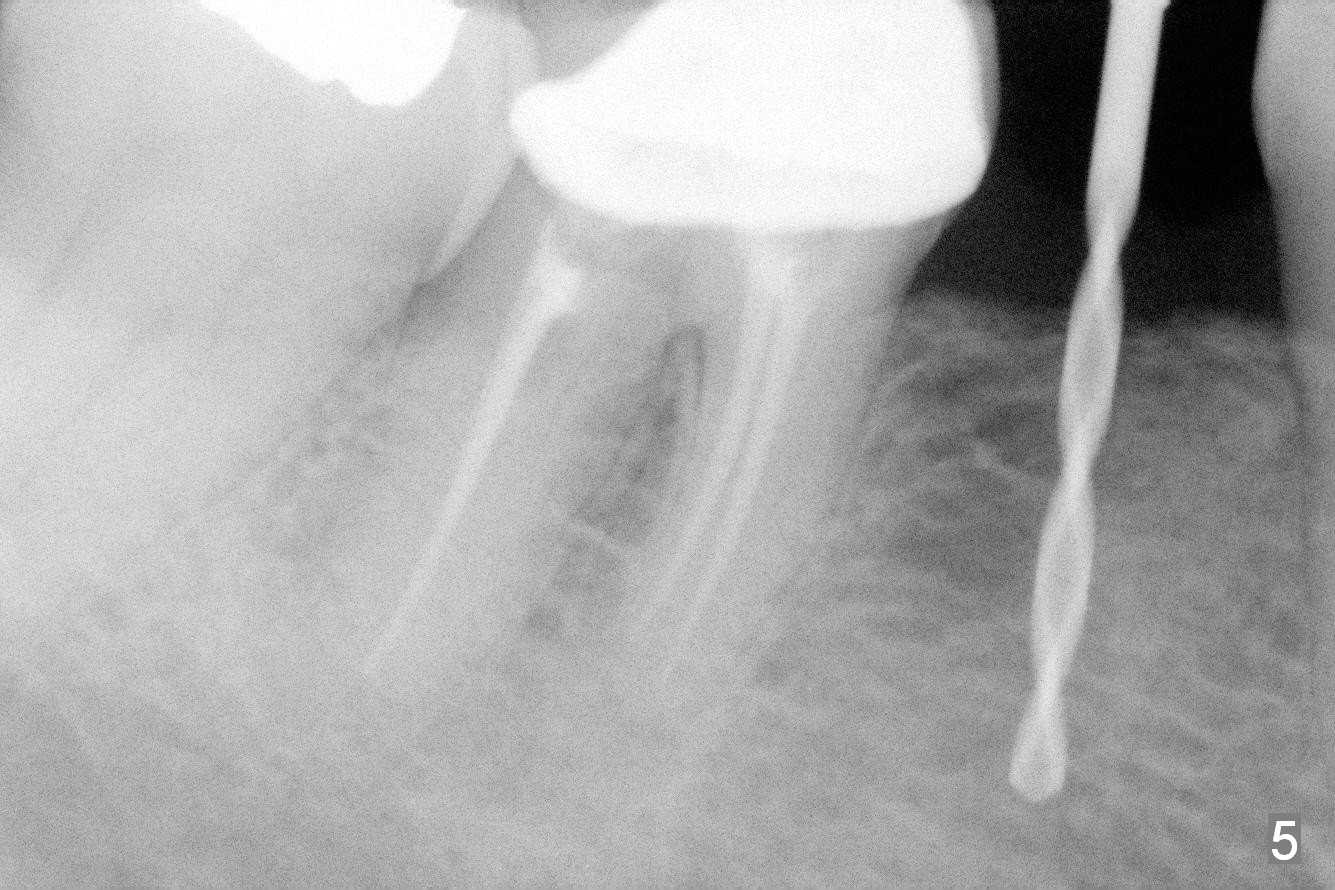
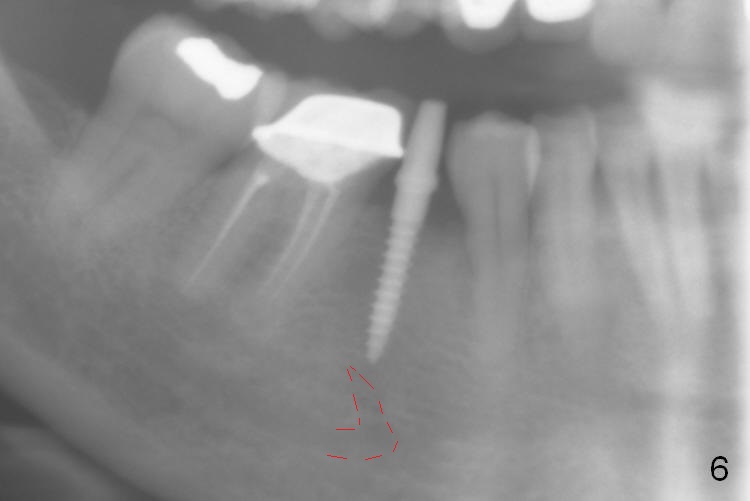
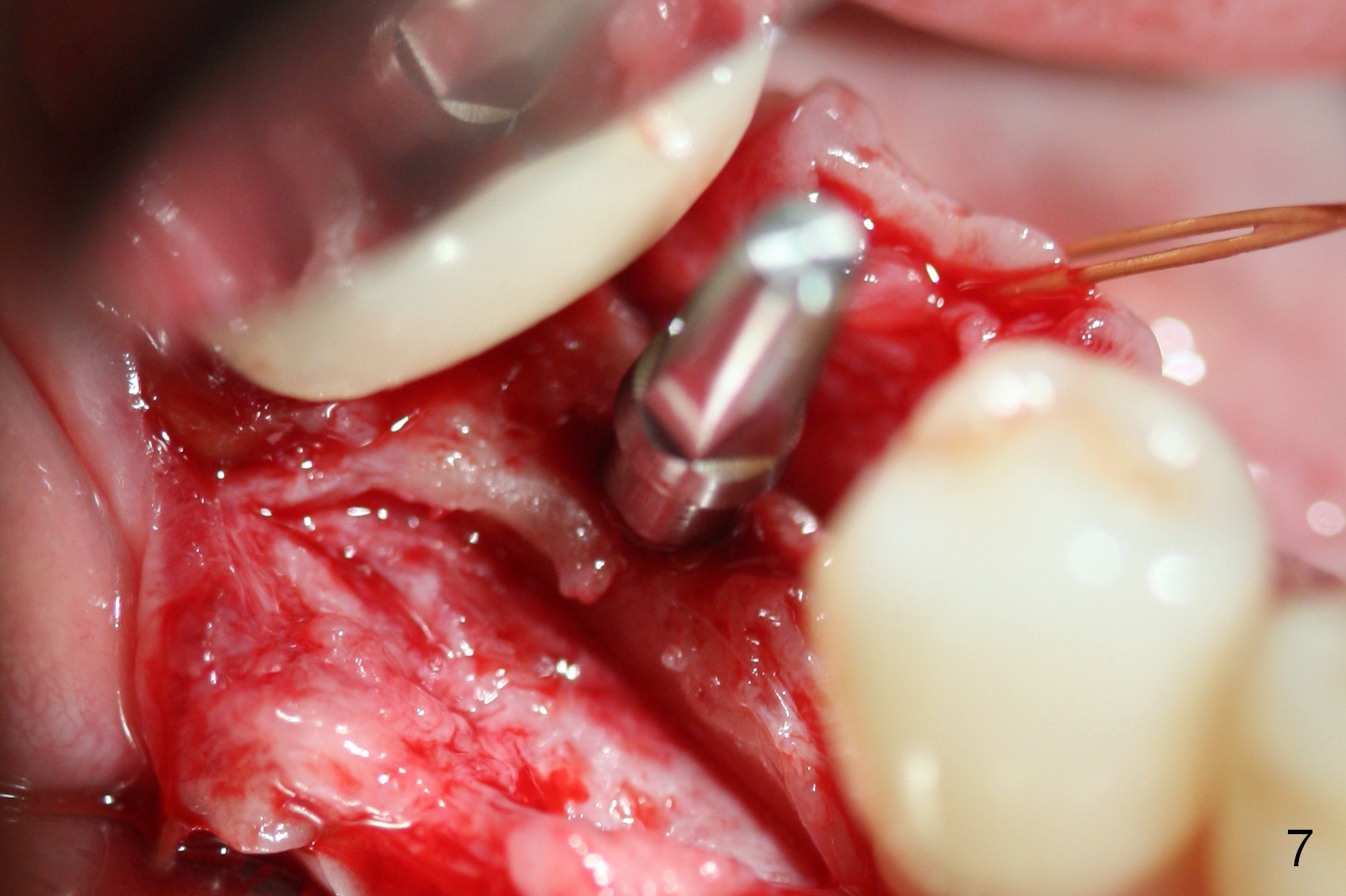
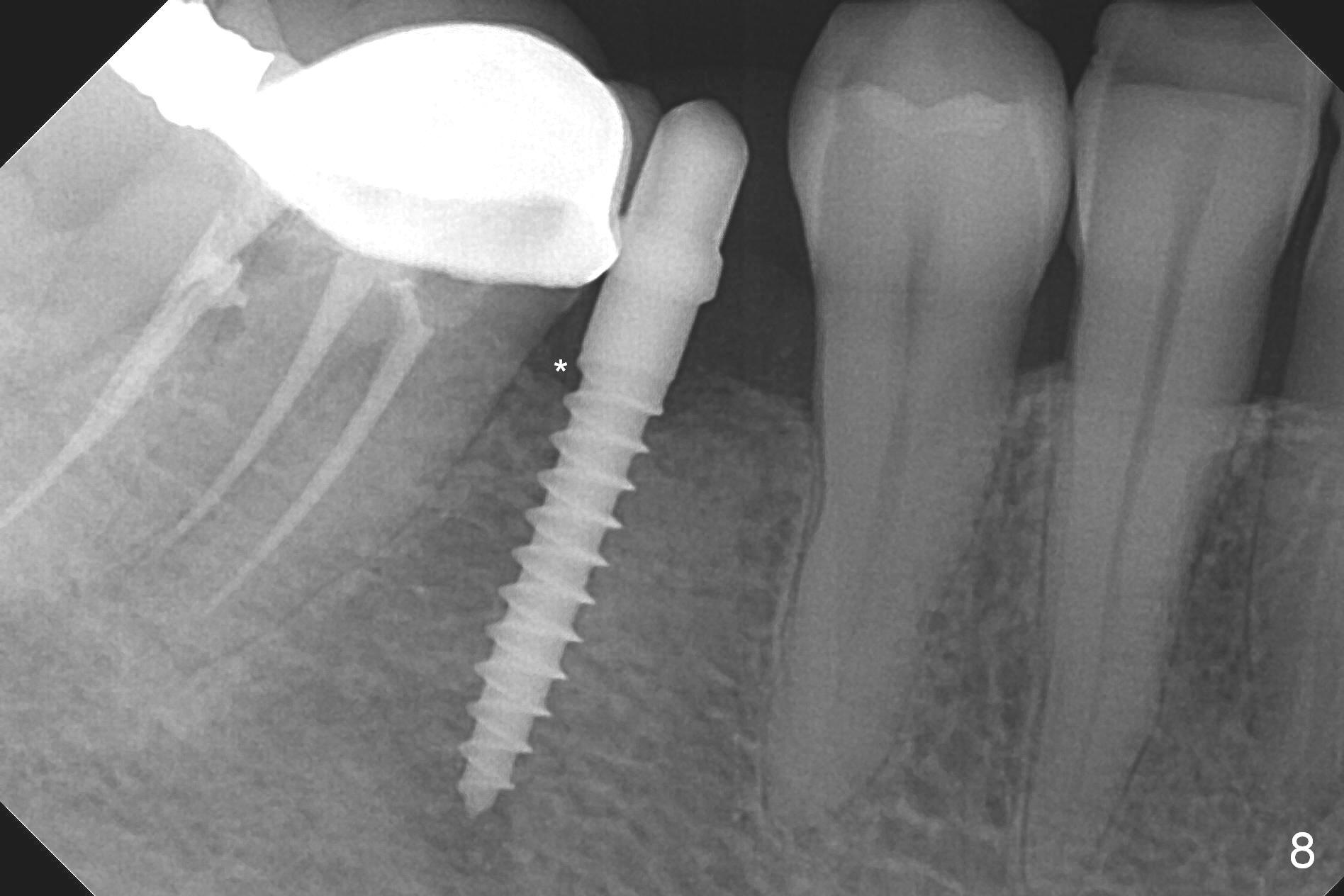
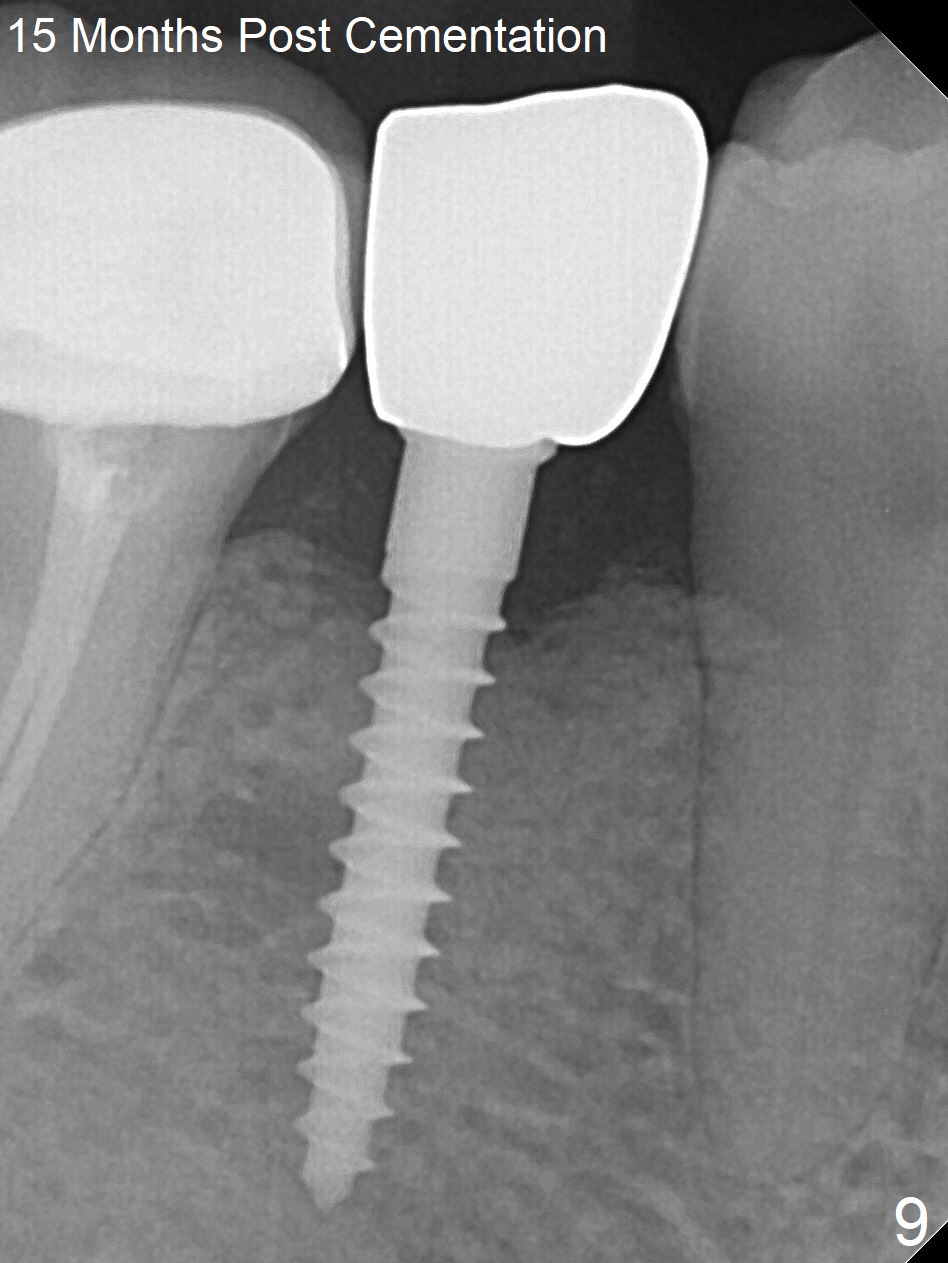
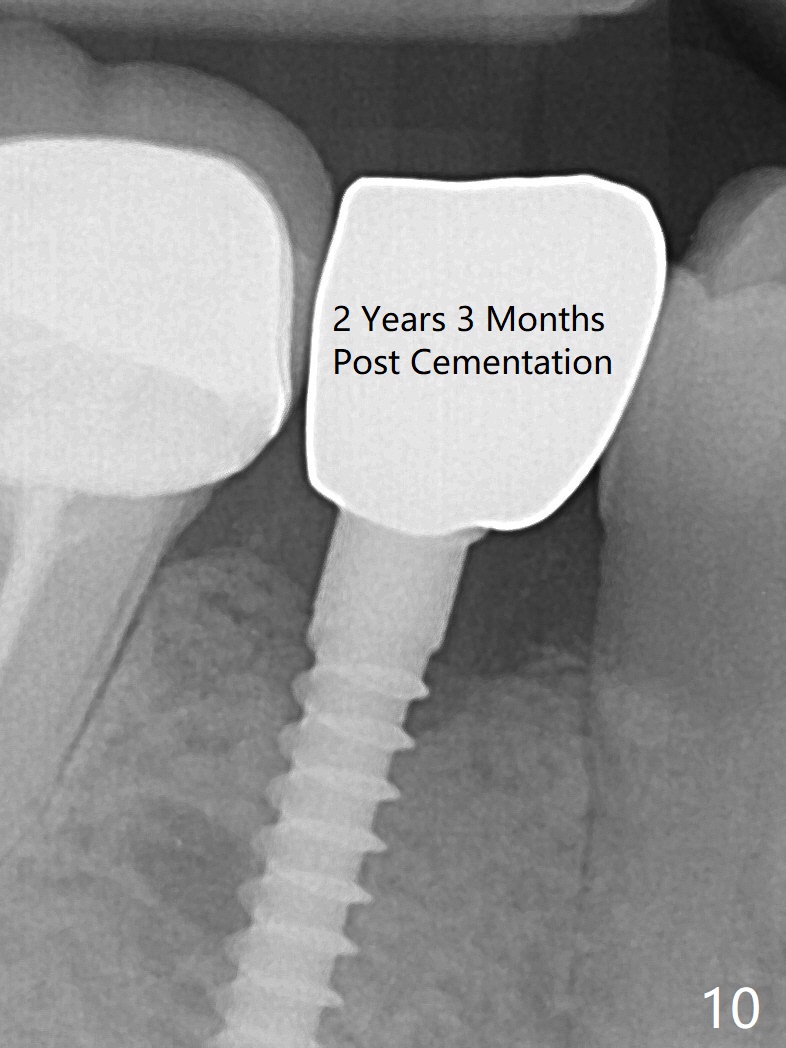
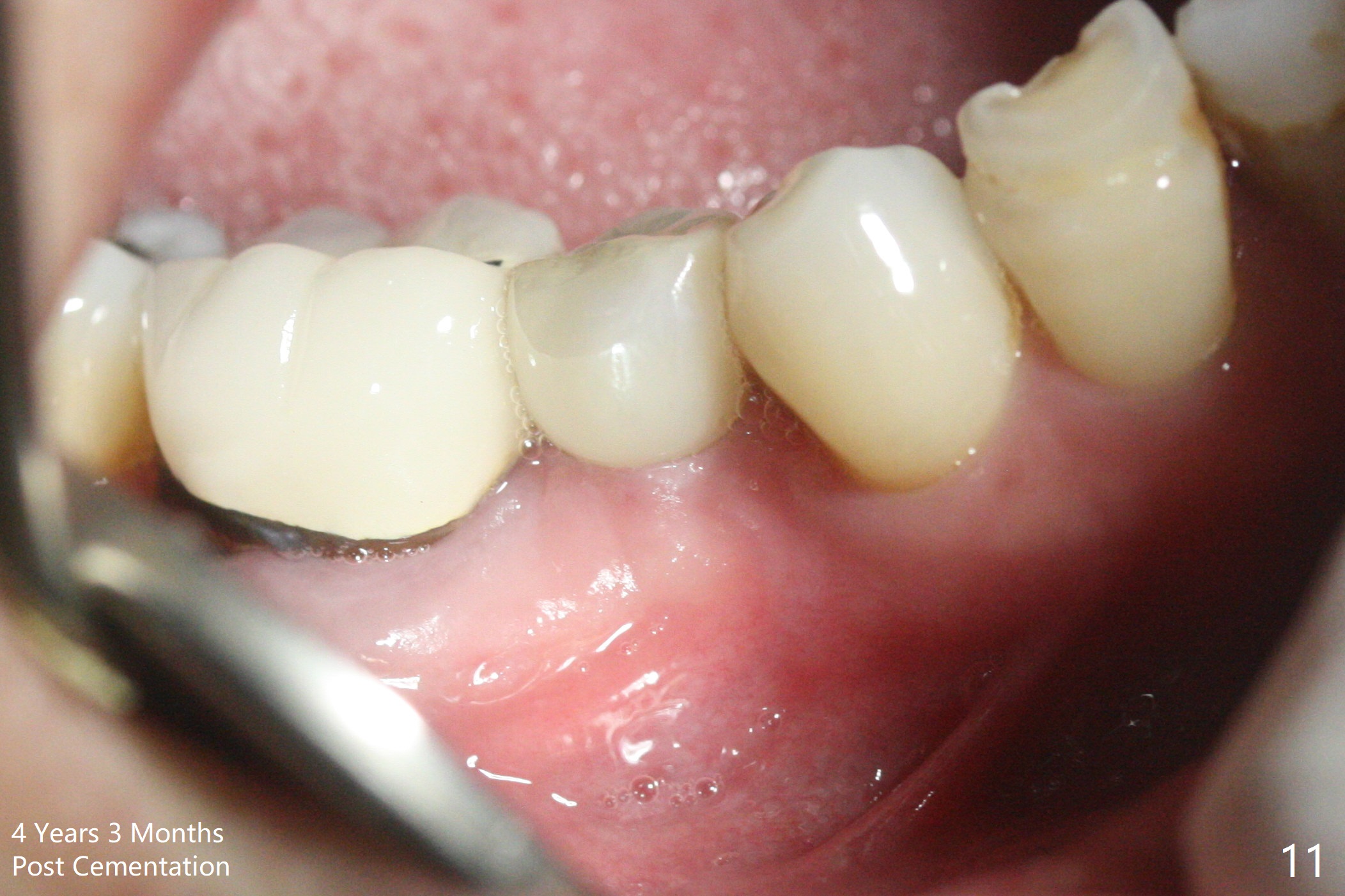
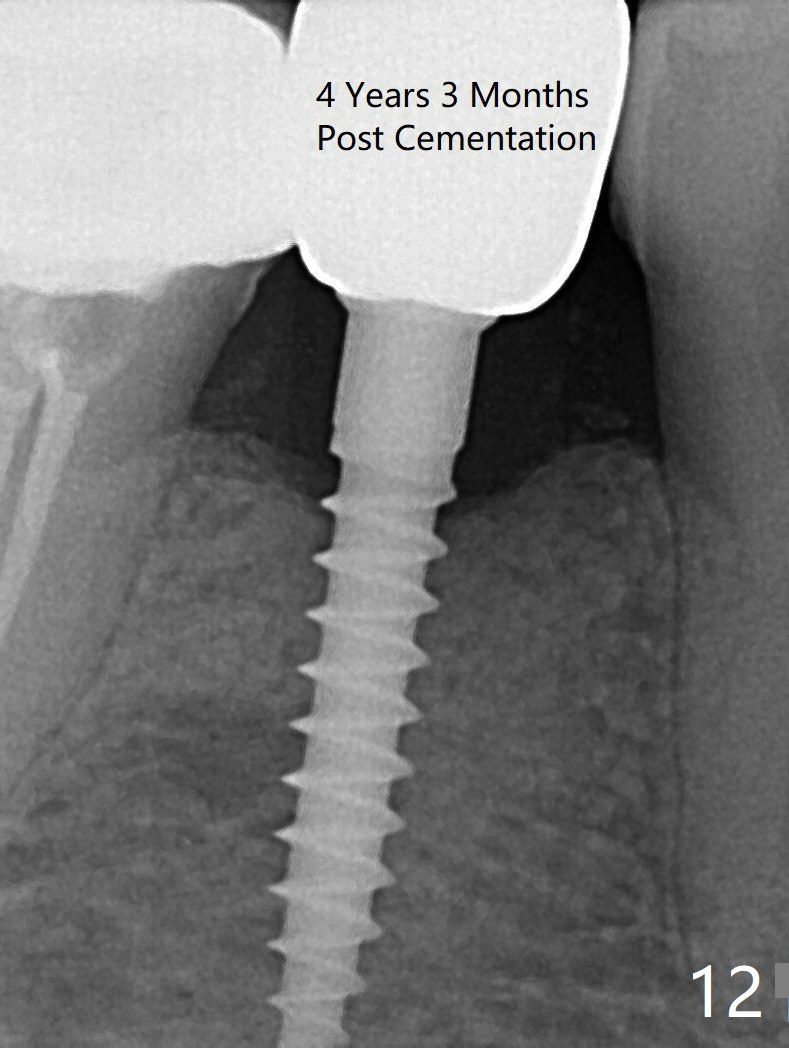
Preop photo shows the distal inclination of the tooth #28 (Fig.1). The distal surface of the latter is reduced before incision for implant placement at #29 (Fig.2). The buccolingual width is approximately 4 mm, as compared to 3 mm implant positioner (Fig.3). After 1.2x10 mm osteotomy (Fig.5), the mesiodistal cortical bone is removed with a small high-speed fissural bur (Fig.4). When a 2.5x12(2) mm 1-piece implant is placed (Fig.6), there is no buccal (Fig.7) or lingual plate perforation. There is no postop paresthesia. There is mild bone loss distal 4 months postop (Fig.8 *). Take photos before and after permanent crown cementation to show increase in ridge width after bone graft and improvement in gingival health after provisional modification. Take PA and/or BW post cementation to show that the distal bone resorption (Fig.8 *) is partially due to angulation. No continuous bone loss 15 months post cementation (Fig.9). There is mild bone resorption mesially 2 years 3 months post cementation (Fig.10). The soft and hard tissues remain healthy 4 years 3 months post cementation (Fig.11,12).
Return to Lower Prmolar Immediate Implant, IBS 劈开术Xin Wei, DDS, PhD, MS 1st edition 09/22/2016, last revision 05/10/2021