,%20bone%20graft.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
 |
 |
 |
,%20bone%20graft.jpg) |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
.jpg) .jpg) |
Calculate Implant Length
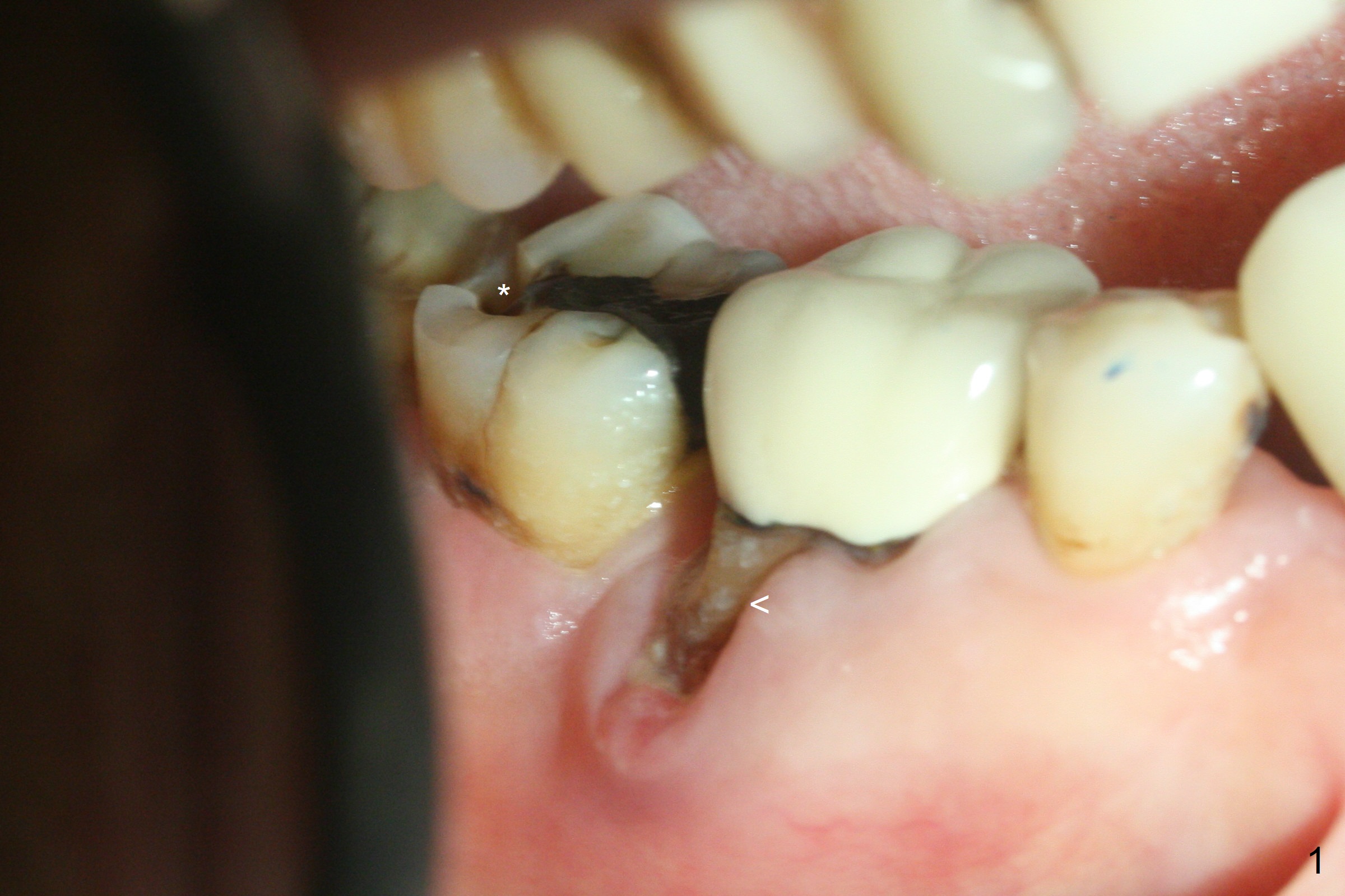
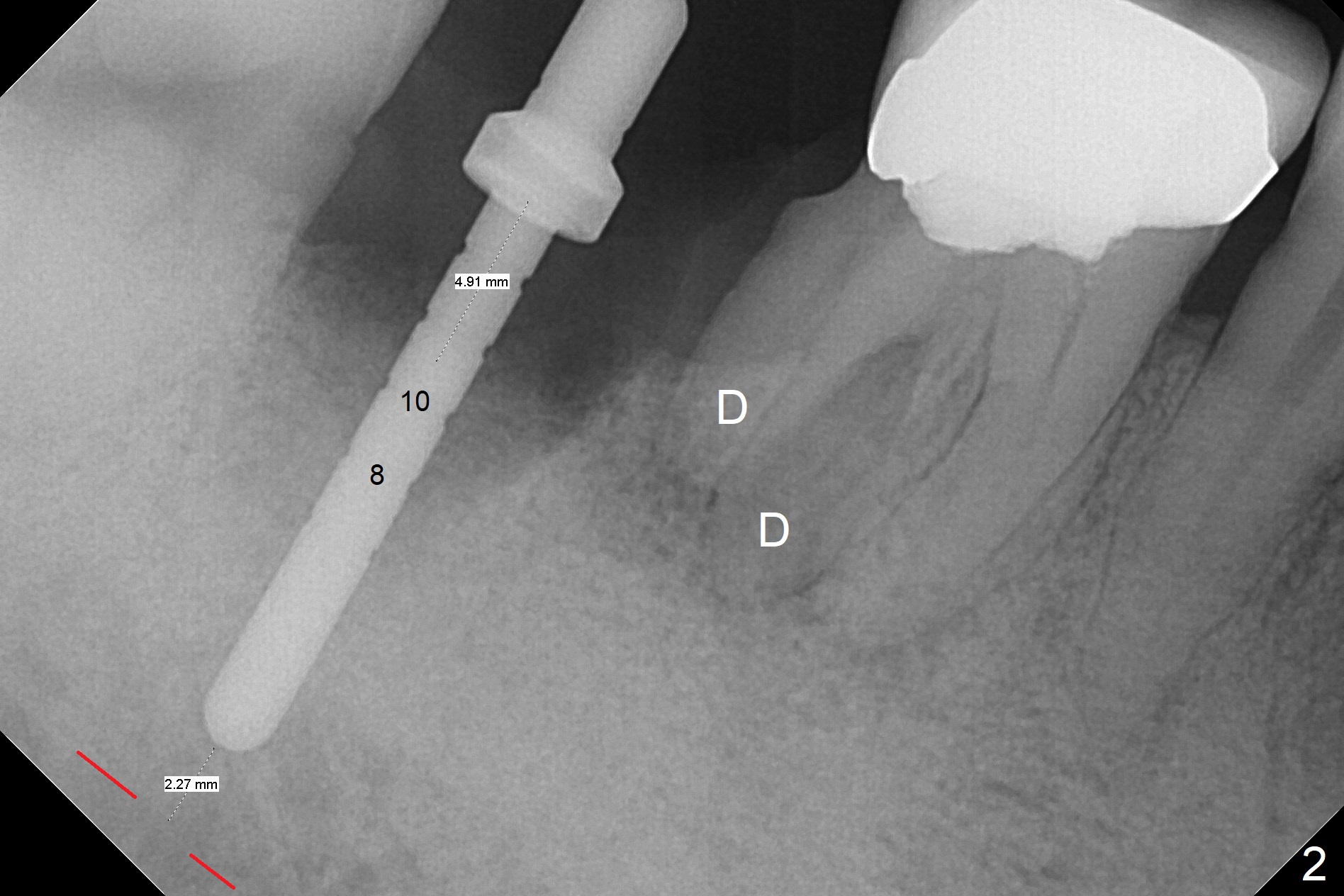
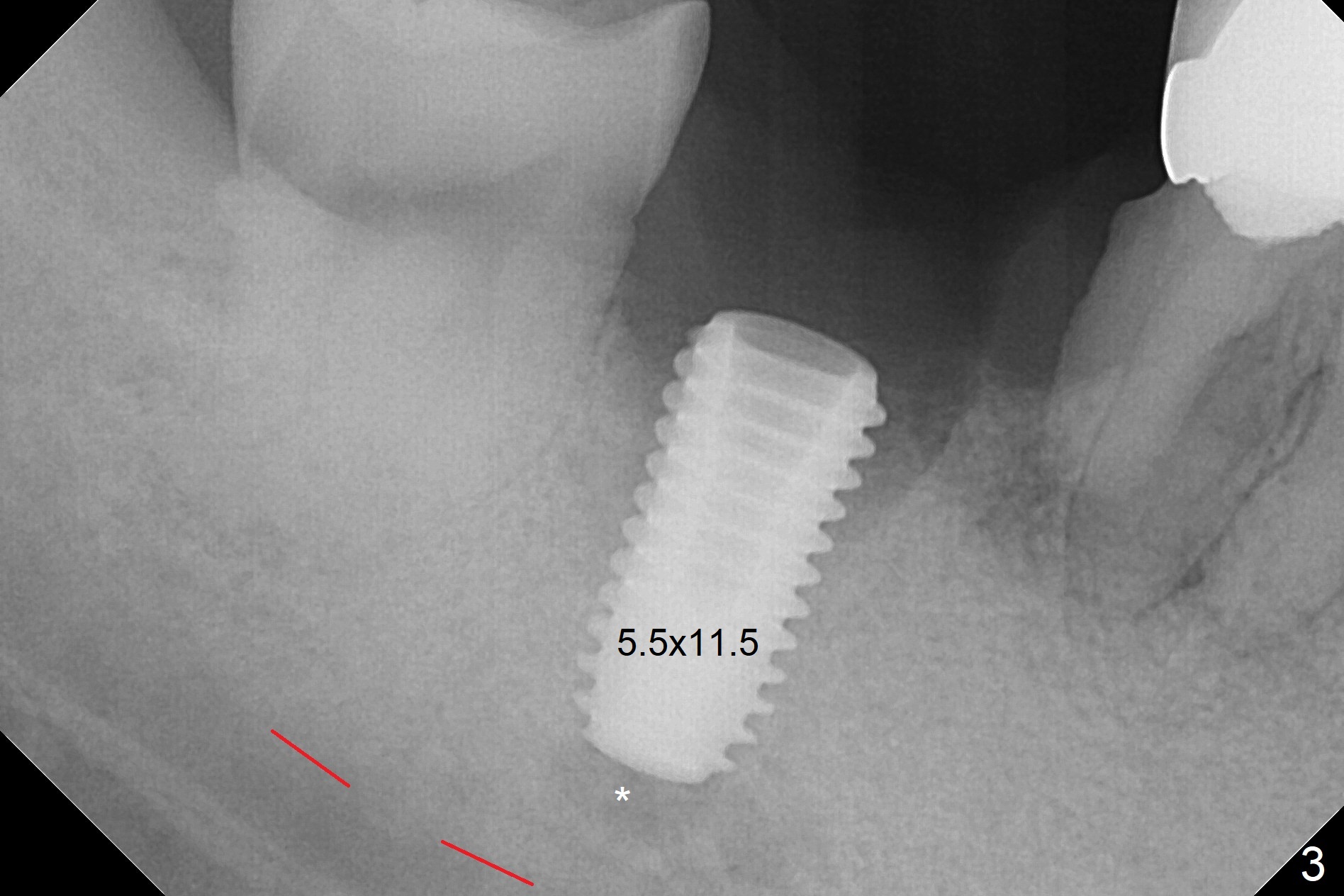
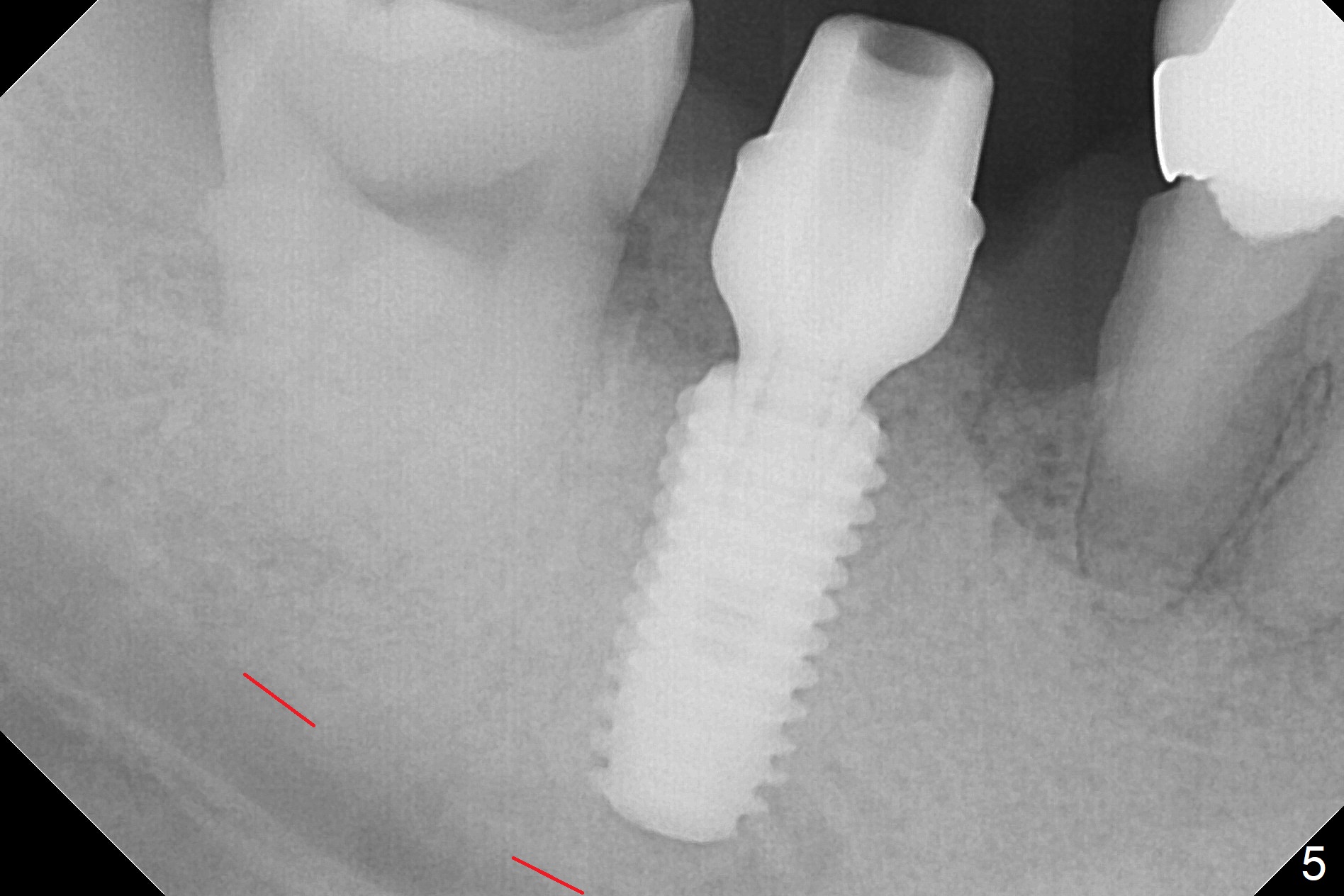
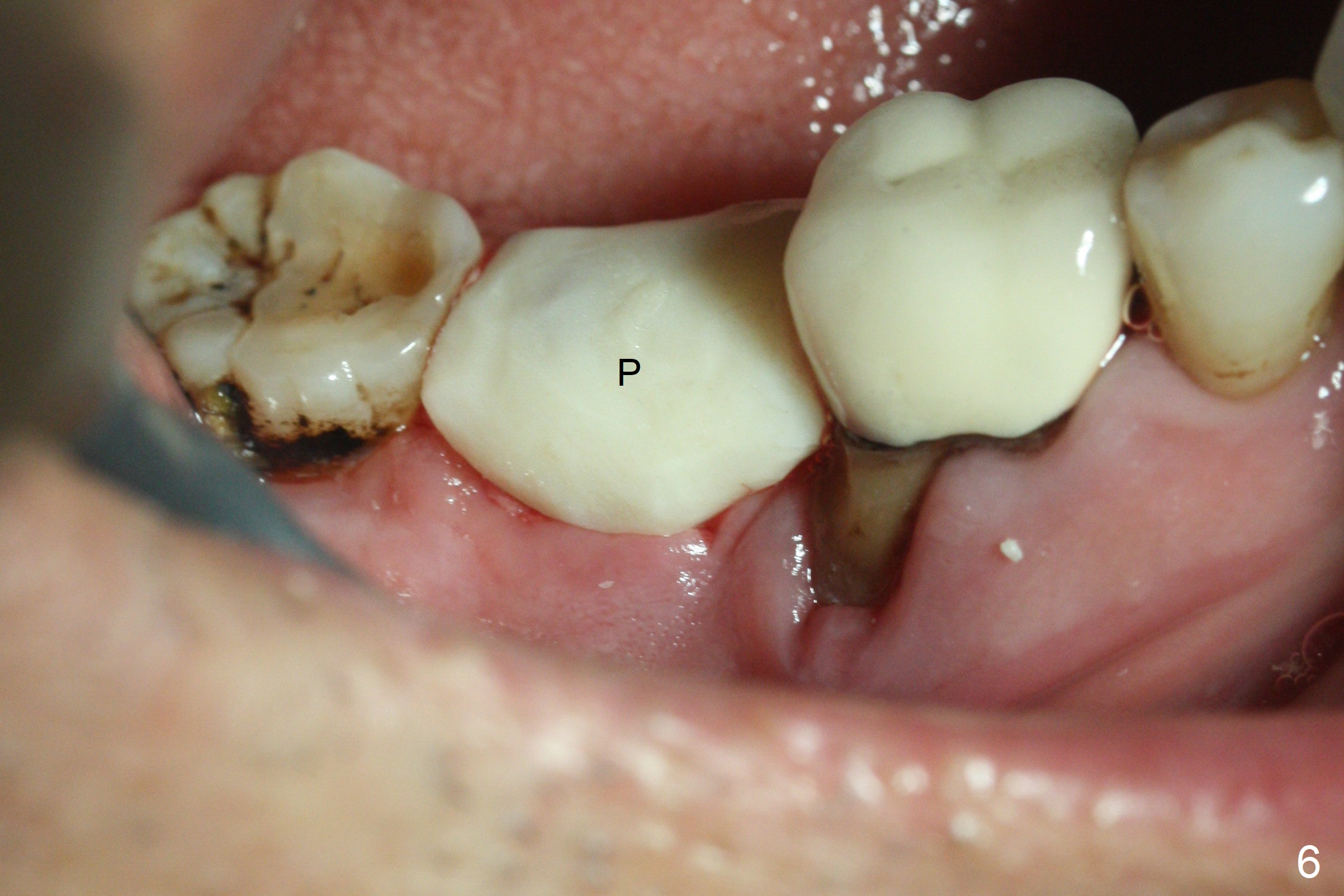
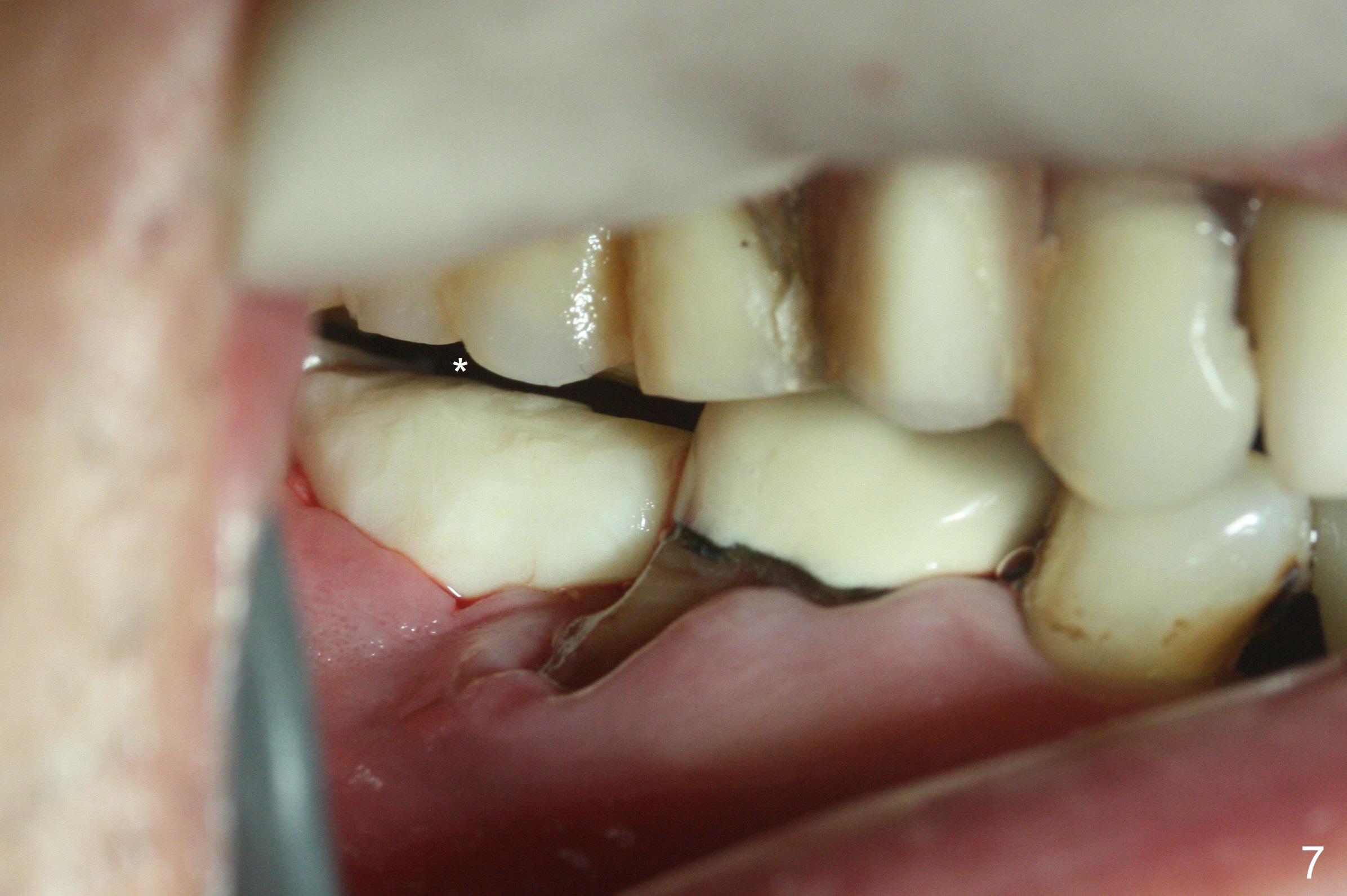
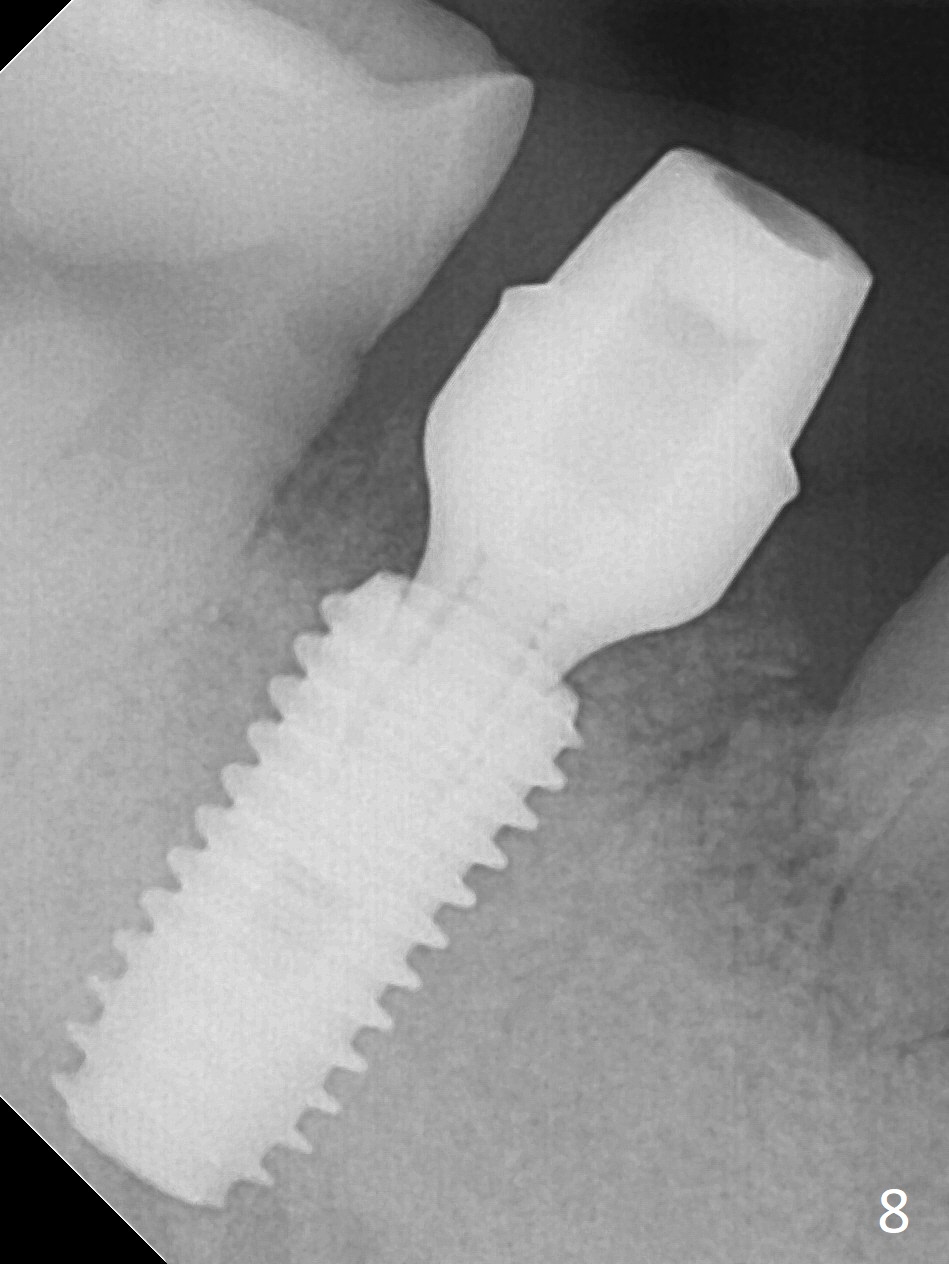
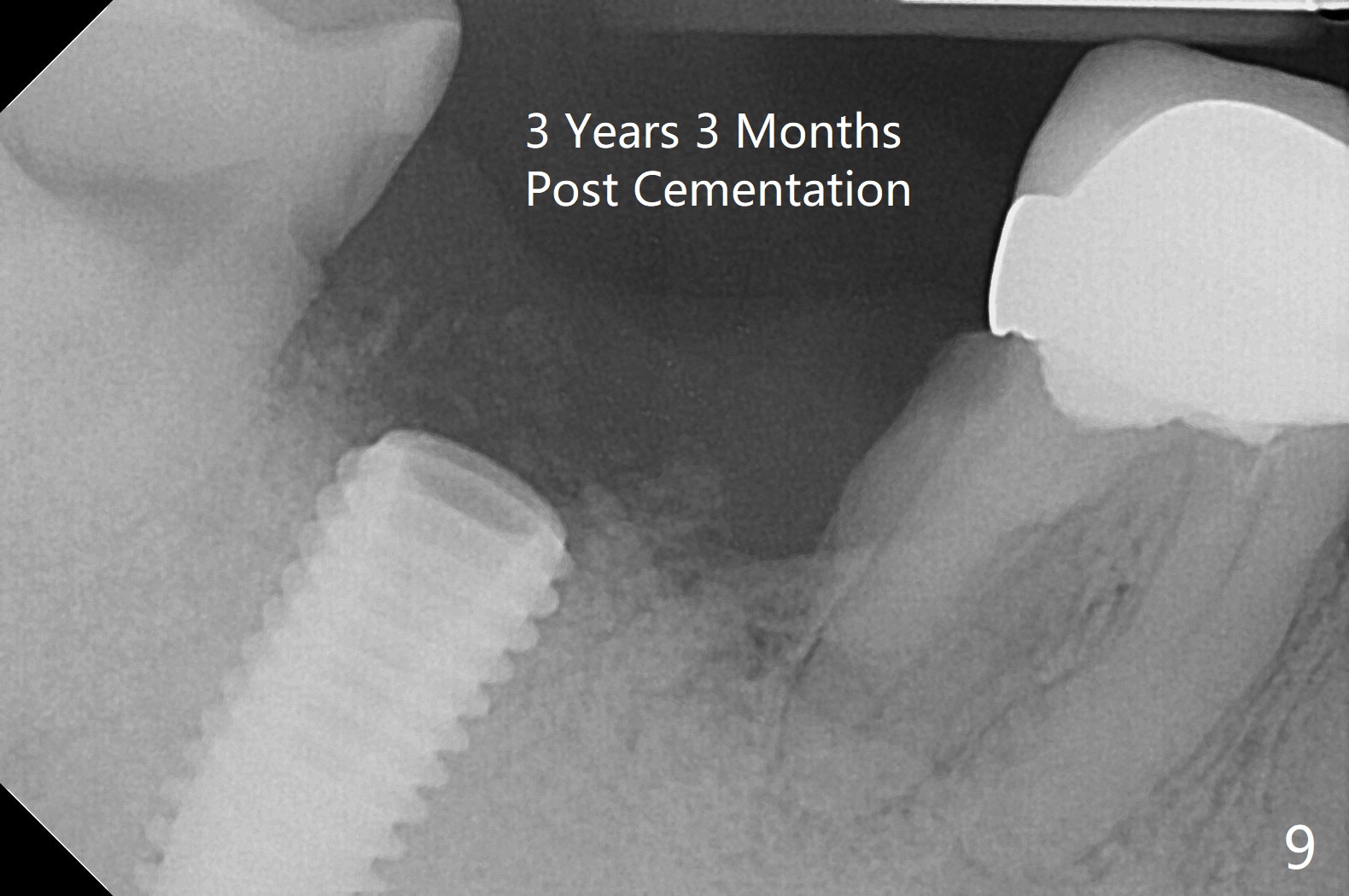
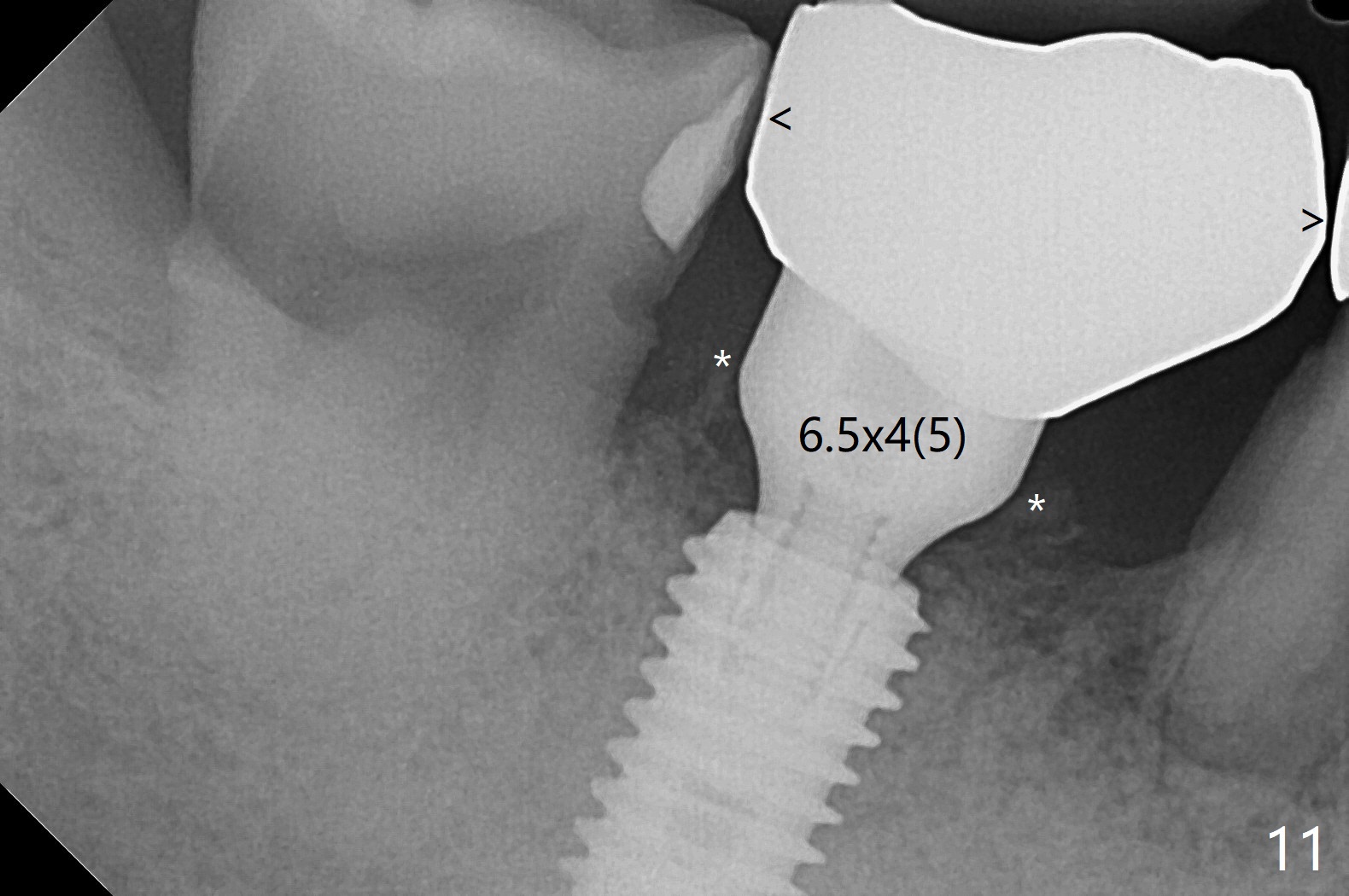
Although the tooth #30 has distobuccal root exposure (Fig.1 <), it is asymptomatic. In contrast the tooth #31 with the distoocclusal caries (*) is symptomatic. After use of 2 mm drill for 18 mm (lingual gingival margin), a calculated parallel pin is inserted (Fig.2 (D: 2 distal roots of the tooth #30)). It appears that a 11.5 mm long implant is appropriate for the site; a 5 mm cuff is expected. Following 4.8 mm drill, a 5.5x11.5 mm implant is placed initially (Fig.3) with an apical space (*) and clearance from the Inferior Alveolar Canal (red dashed line). The implant is placed deeper with placement of a 6.5x4(5) mm abutment and bone graft (*, Fig.4,5). After placement of collagen membrane over the graft, an immediate provisional is fabricated (Fig.6 P) with clearance from the opposing tooth (Fig.7 *). There is no bone loss 3.5 months postop (Fig.8). In fact the abutment has not been seated completely since its placement (Fig.4,5,8). The crown/abutment dislodges 3 years 3 months post cementation (Fig.9). The latter occurs for long incubation time because of opposing partial denture (Fig.10). After trimming proximal surfaces (Fig.11: arrowheads), the abutment remains incompletely seated (Fig.11) due to possible crestal bone interference (Fig.11 *). The smaller abutment by itself remains unseated (Fgi.12). One size small one is completely seated (Fig.13). Impression is taken. Two weeks later the abutment margin is supragingival. After screw torque at 20 Ncm, the crown is cemented with access hole. Excess cement is removed.
Return to
Lower
Molar Immediate Implant, Prevent
Molar Periimplantitis (Protocols,
Table),
IBS
Torque
6
Xin Wei, DDS, PhD, MS 1st edition 07/24/2017, last revision 03/24/2021