
%20mm.jpg)
 |
 %20mm.jpg) |
  |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Ortho-Induced Bone Width Increase is Ineffective
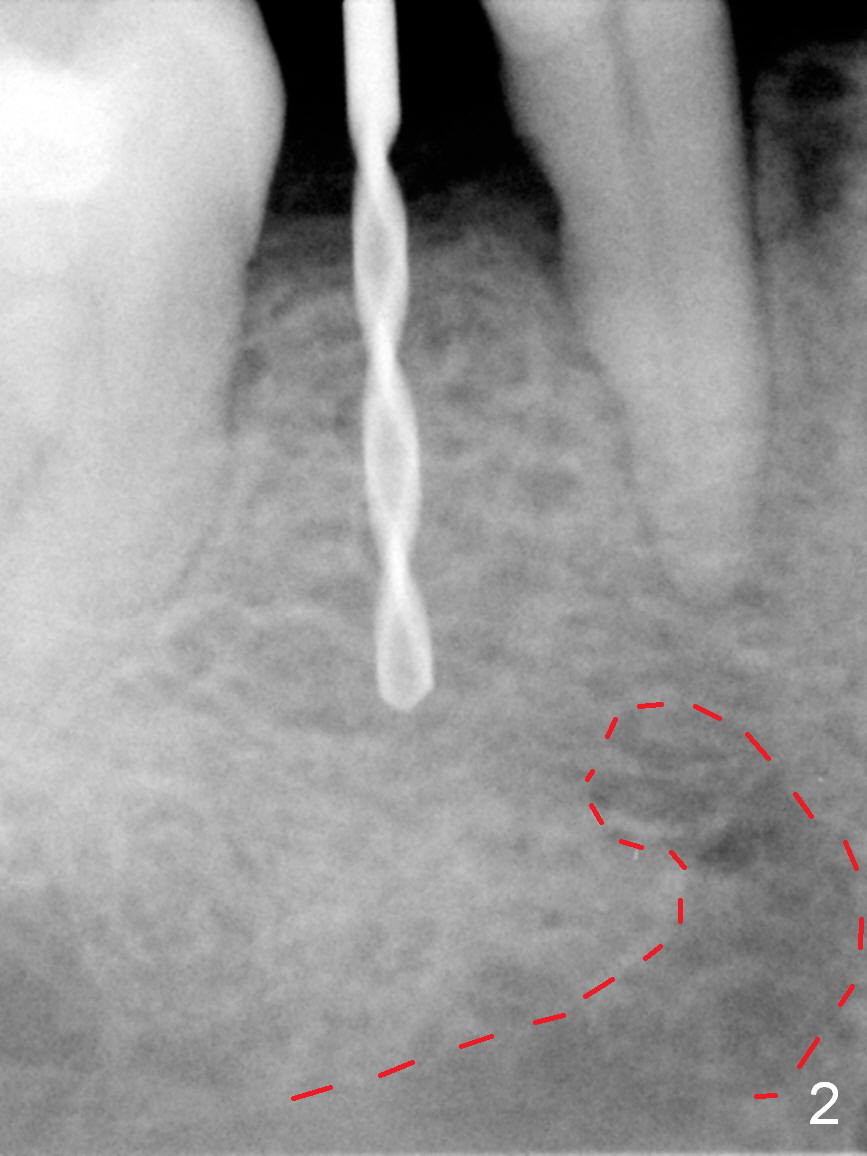
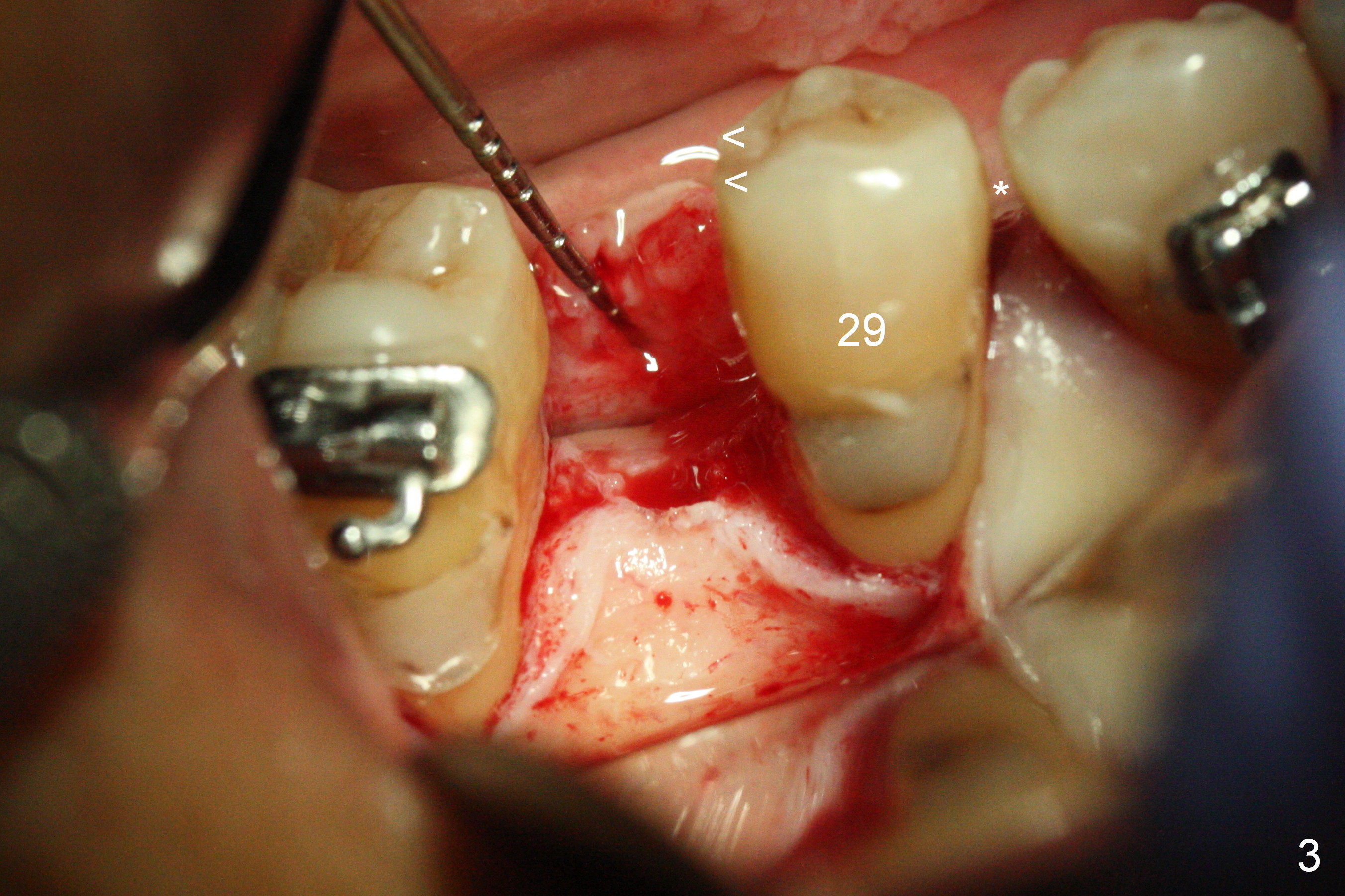
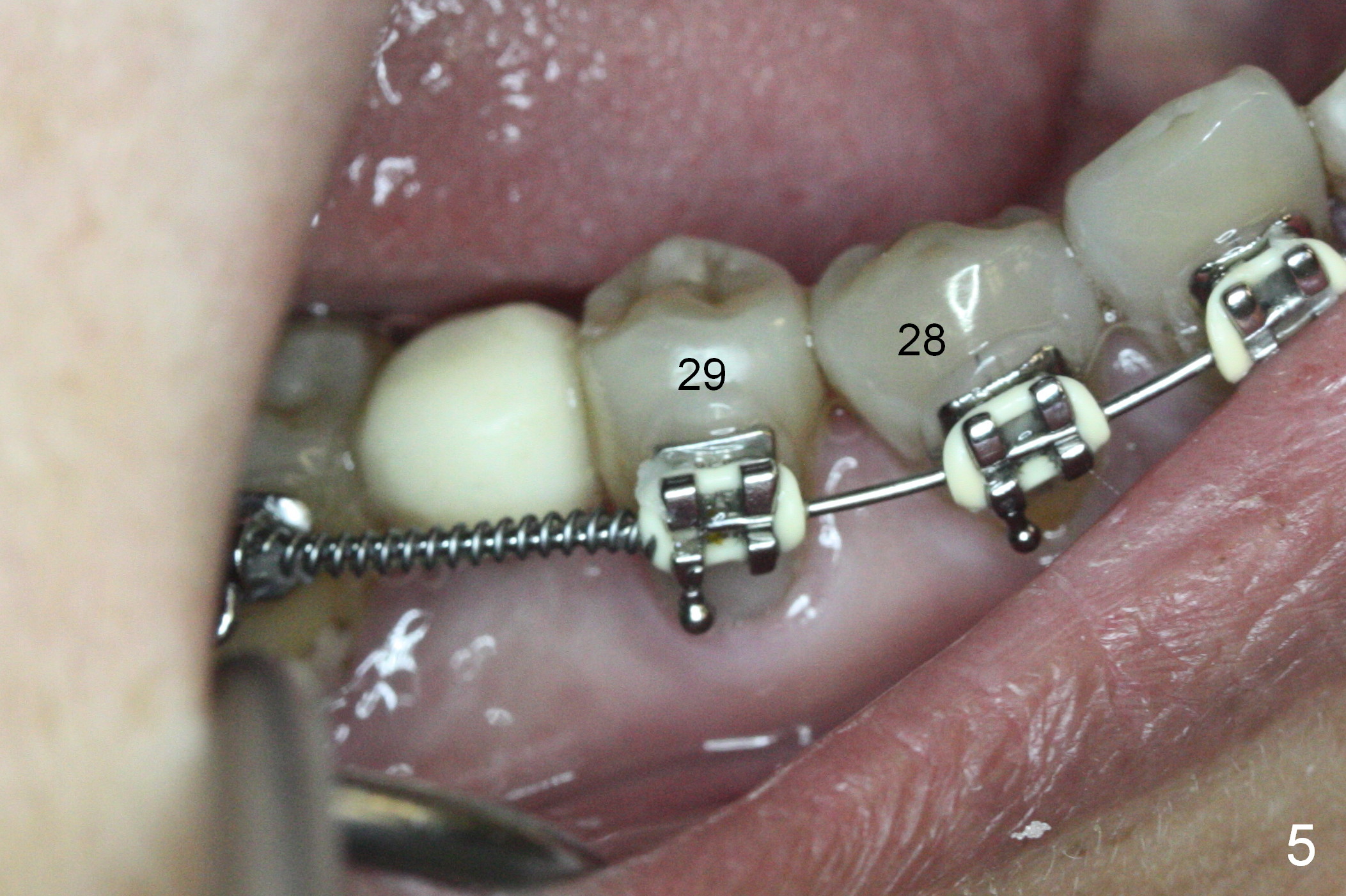
Mesialization of the tooth #29 consists of open coil spring distal (Fig.1 ^) and closed coil spring mesial (^^^). Due to limited time and incompliance, the mesialization is incomplete (Fig.3 *). Total treatment lasts 1 year. The mesial surface of the #29 (Fig.3 <) and the distal surface of #31 are trimmed before incision. The mesiodistal width increases from 5 mm to 6 mm. In fact the ridge is not too narrow buccolingually when an incision is made (Fig.3). There is bone buccal and lingual to a 2.5 mm osteotomy (Fig.3) after adjustment of its initial one with 1.2 mm pilot drill (Fig.2 (red dashed line: the Mental Loop). A 3x12(2) mm 1-piece implant is placed (Fig.4) with insertion torque > 40 Ncm. GBR is also done to increase ridge width.
Three weeks postop, the diastema between #28 and 29 has closed (Fig.5). In fact, the provisional has to be relined to re-establish the mesial and distal contact.
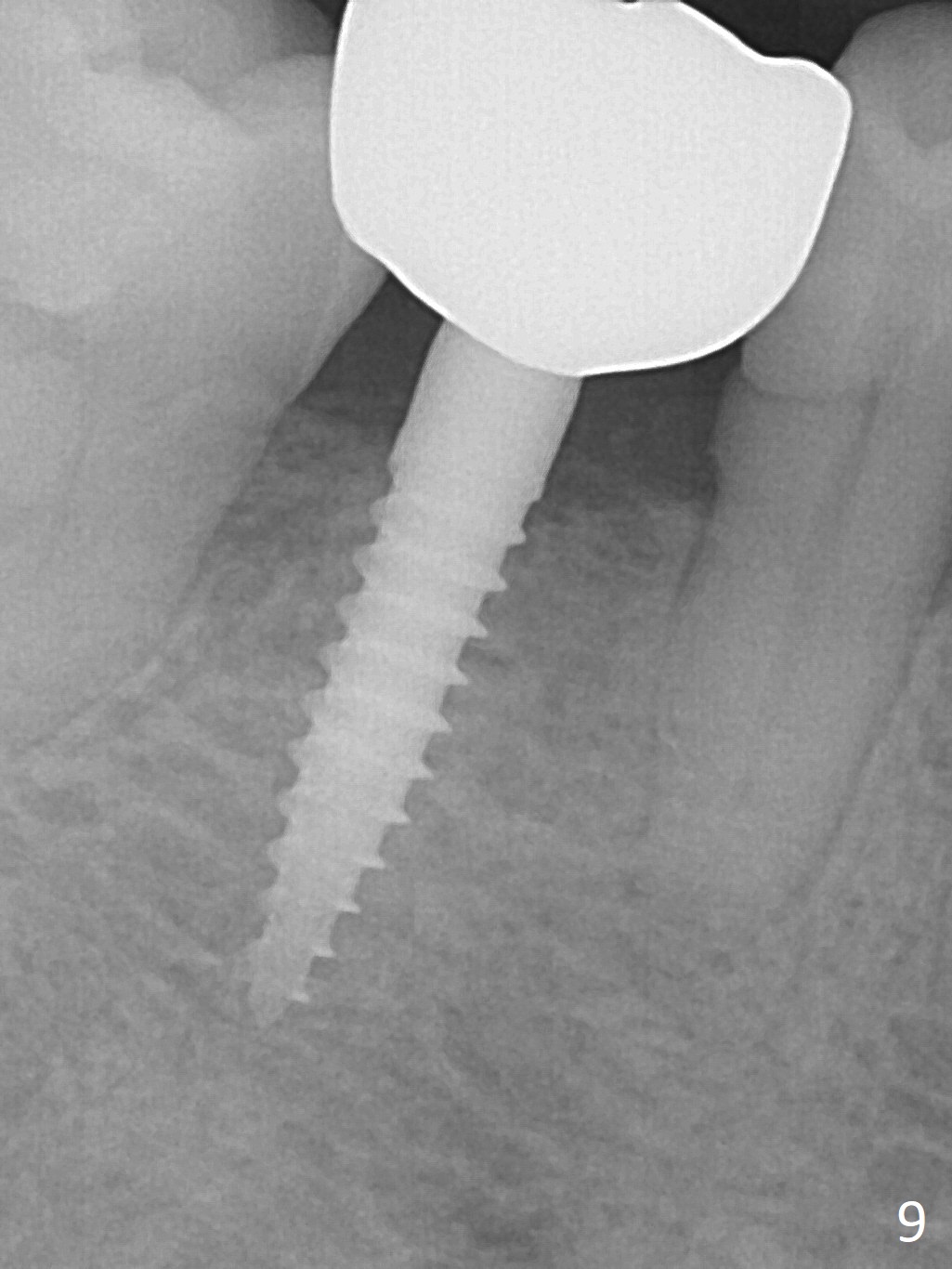
There is no bone loss 3 months postop (Fig.6).
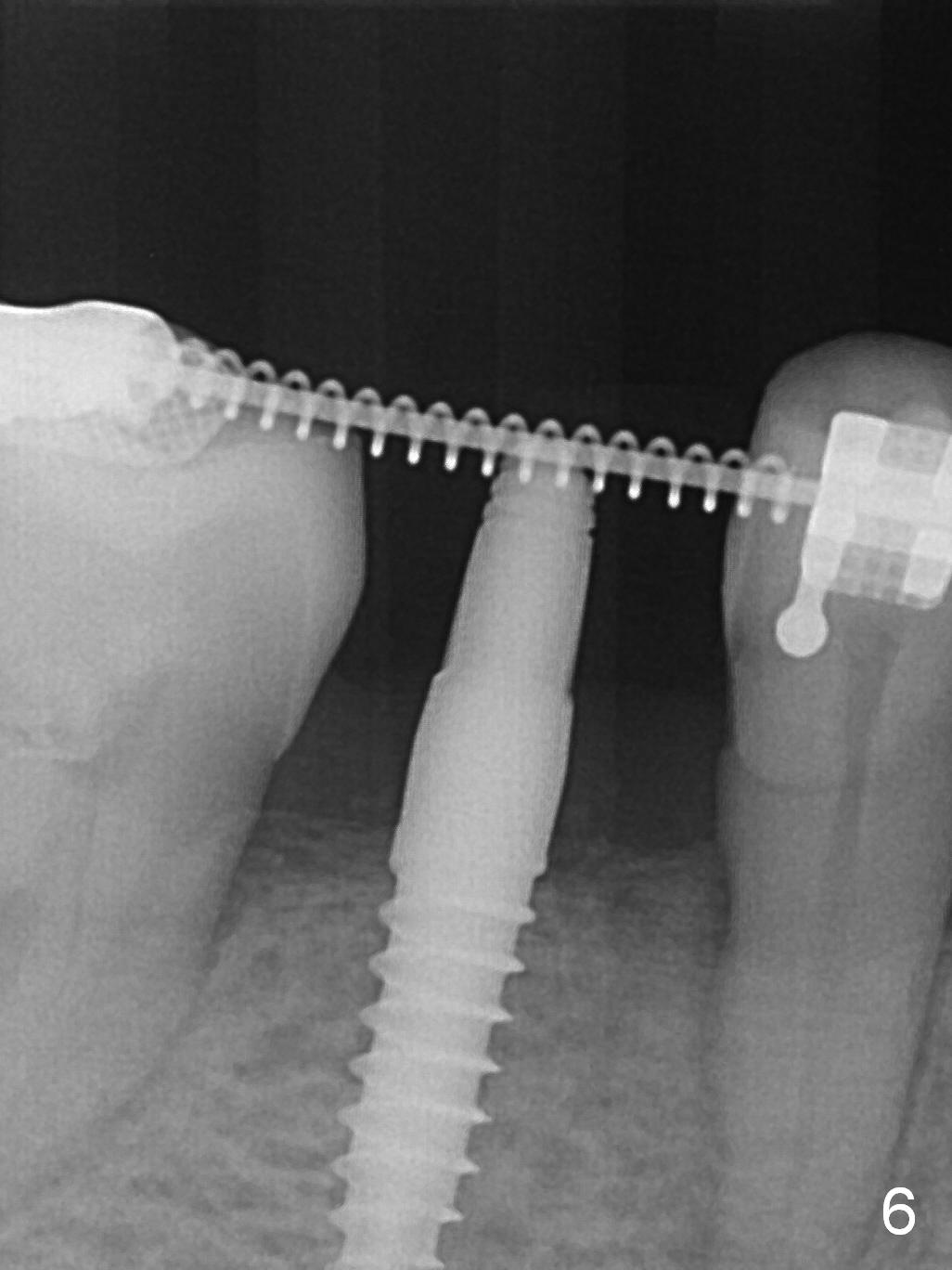
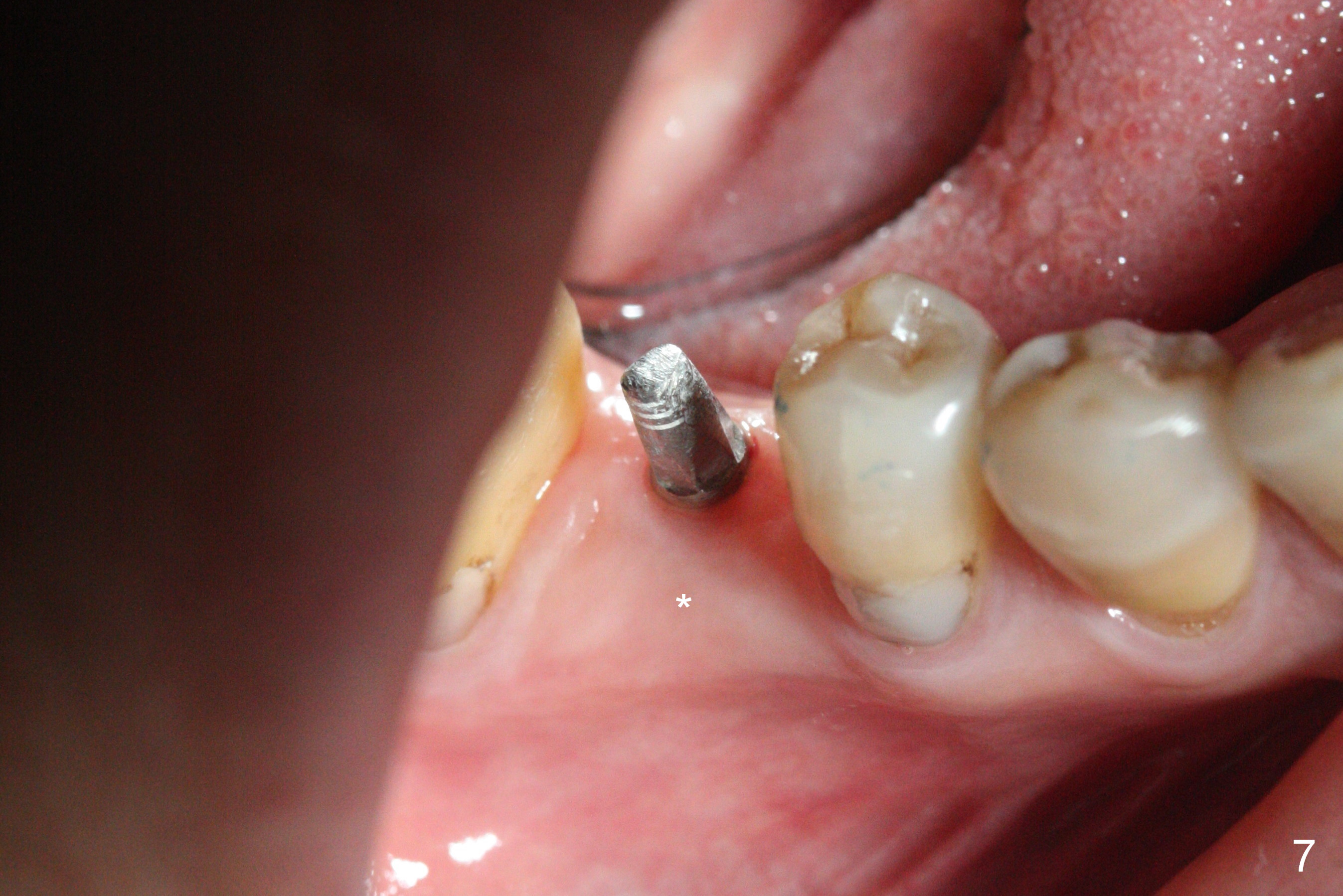
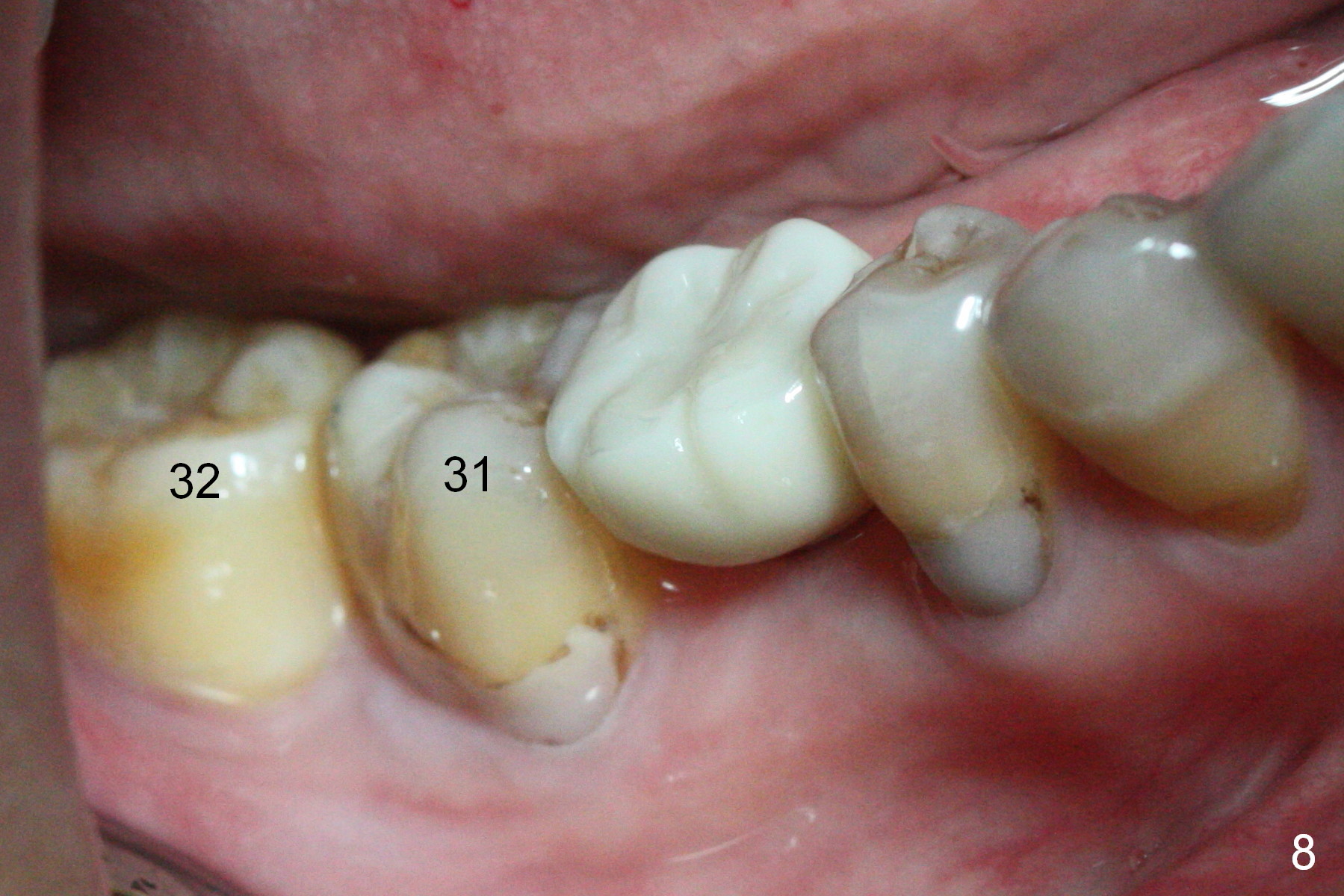
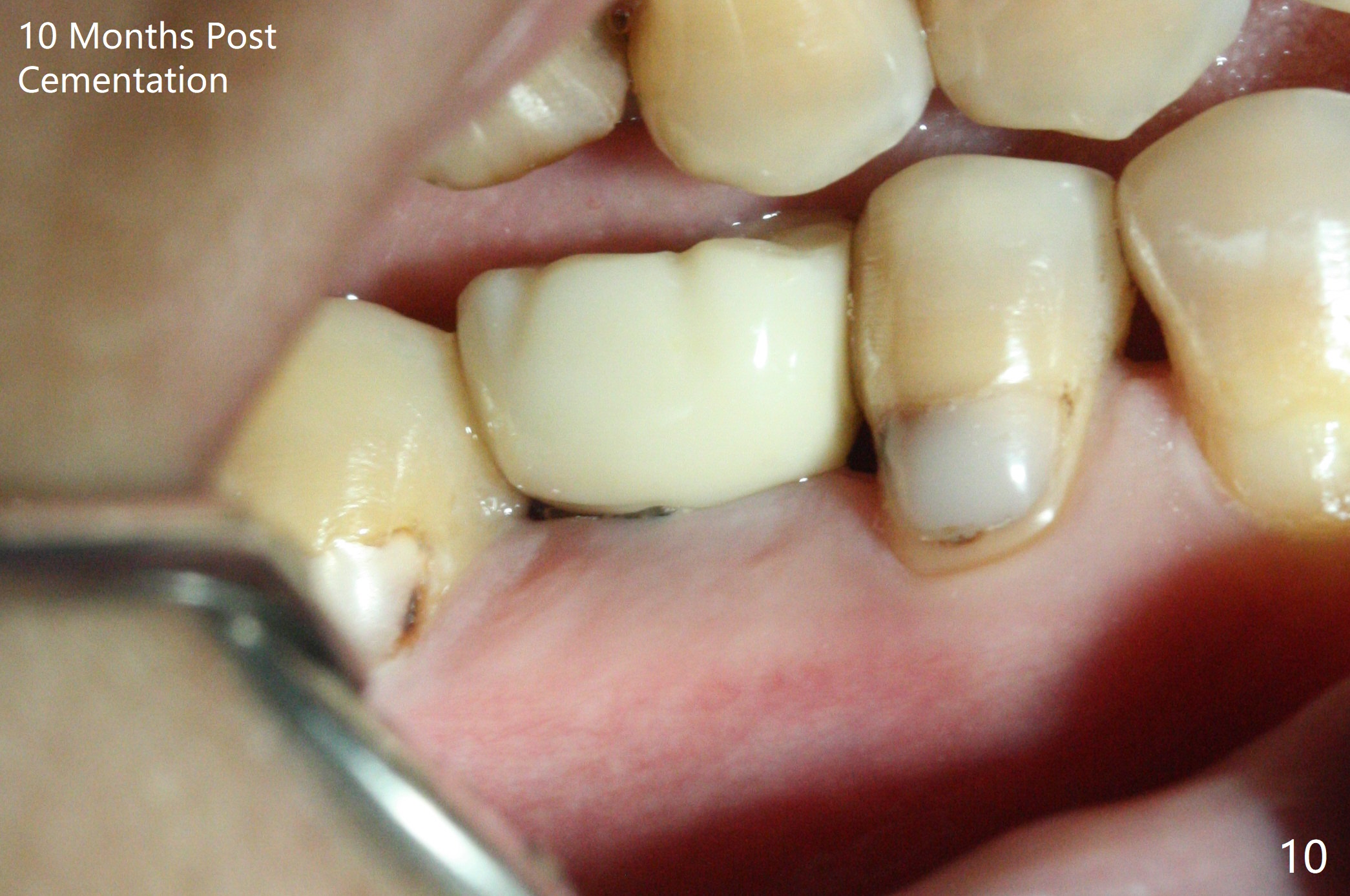
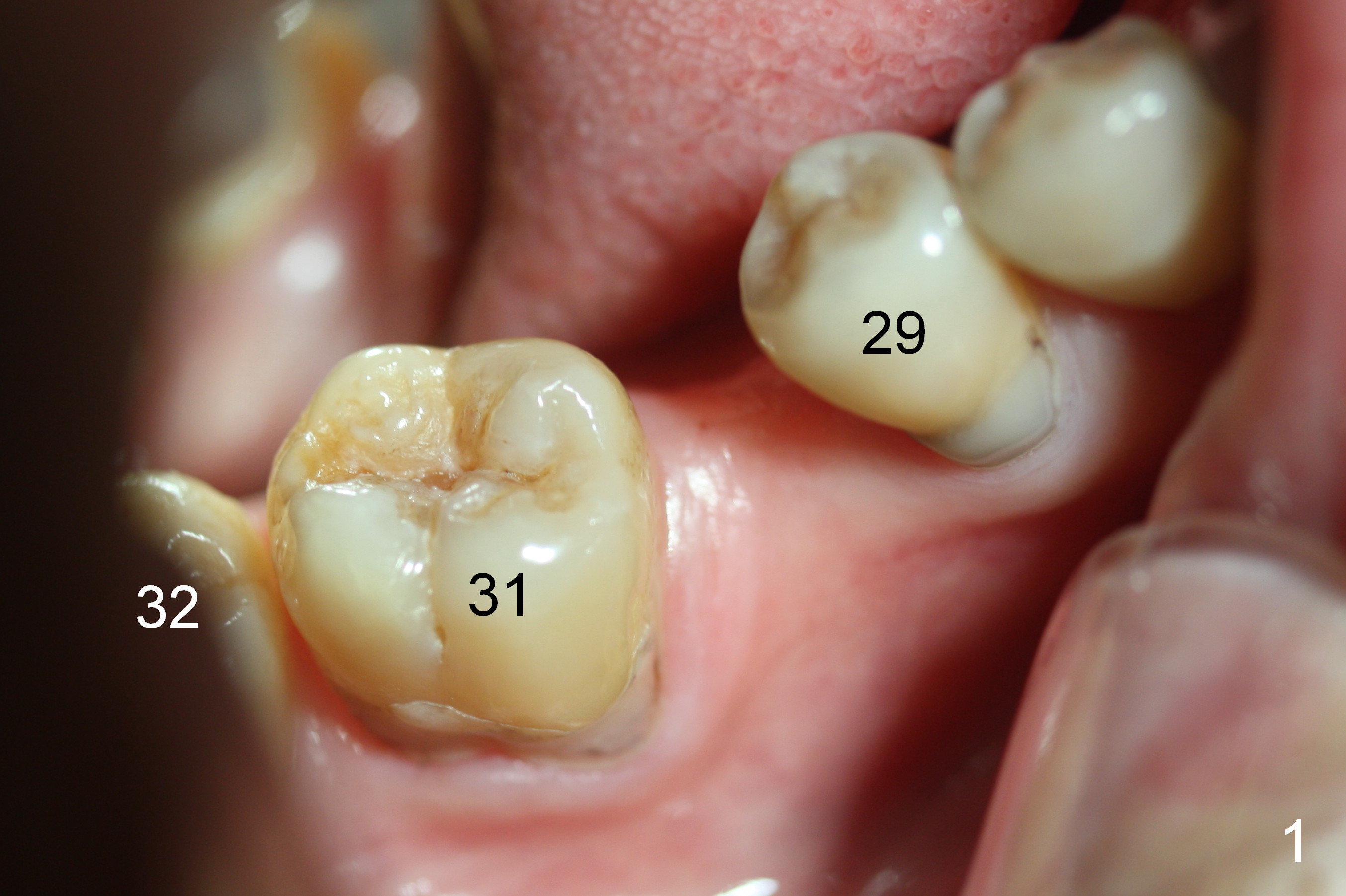
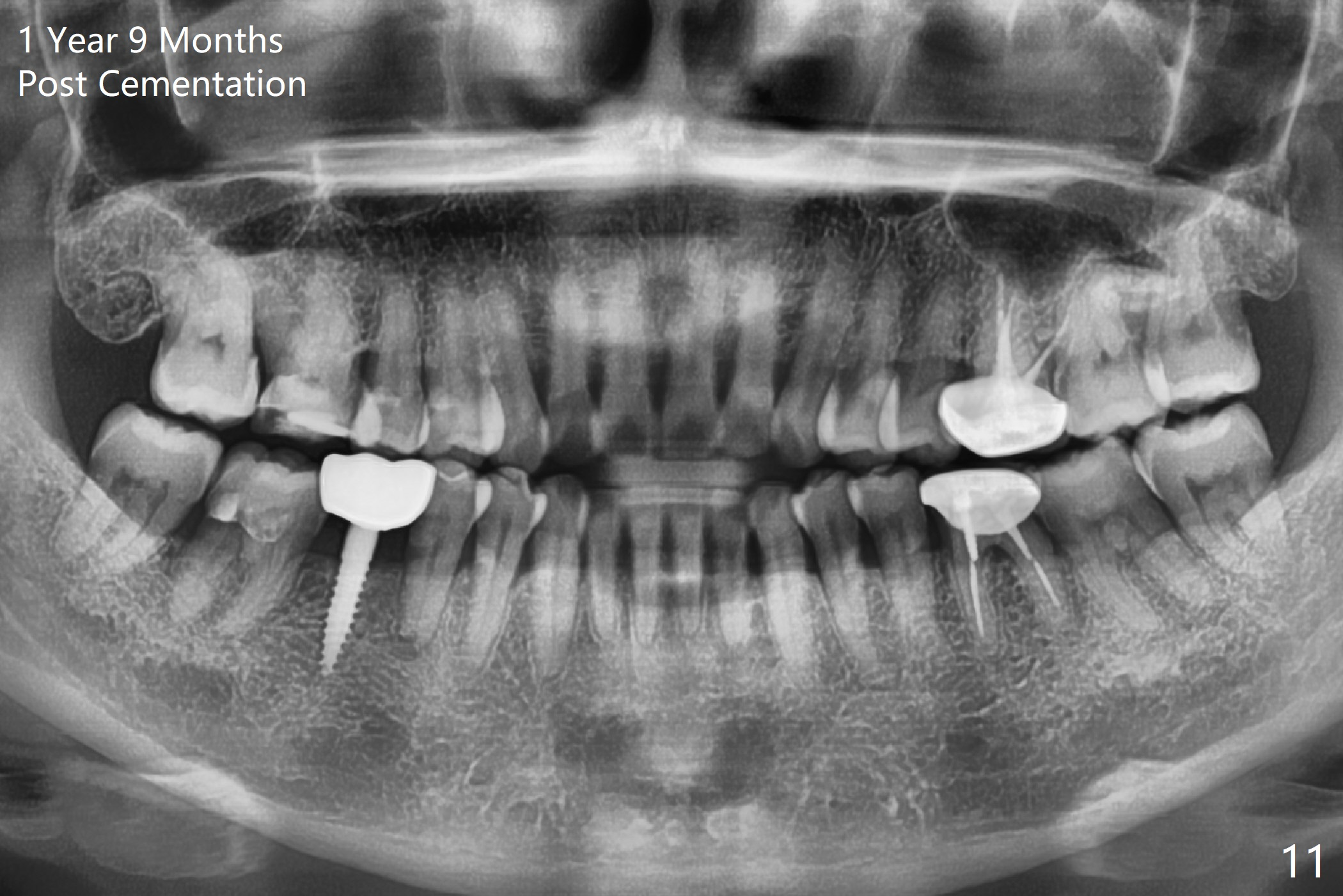
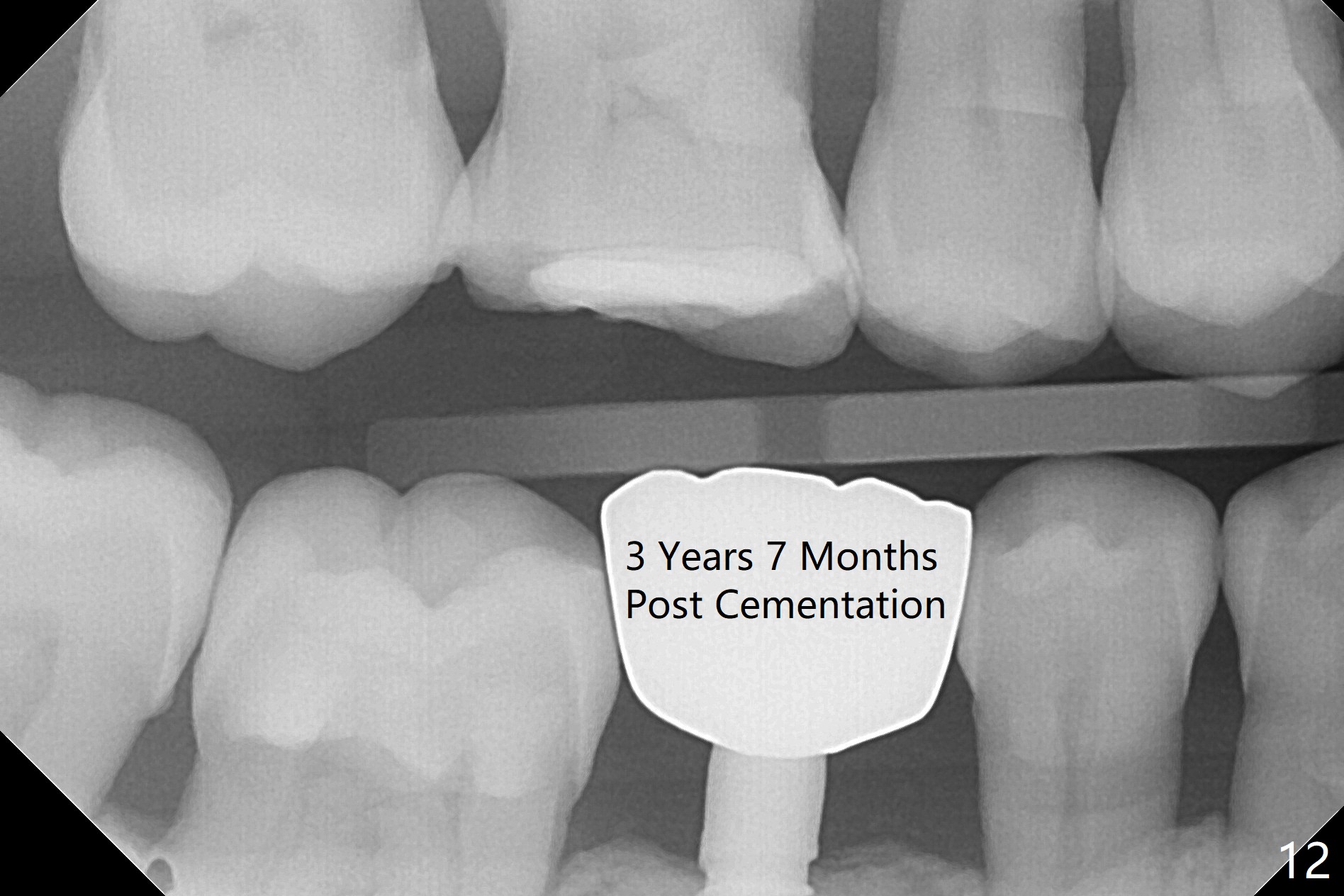
Before crown cementation, the ridge looks wider (Fig.7 *) than preop. There is no diastema between #31 and 32 (Fig.8, 17 days post cementation). The patient is pleased with less food impaction. The total treatment (including ortho) is 16 months. It appears that distalization of #29 is not effective to gain the bone width. In fact simultaneous GBR with implant placement is much more efficient. There is no bone loss 3 months post cementation (Fig.9). The gingiva looks healthy 10 months post cementation (Fig.10). The implant crown is functioning 1 year 9 months post cementation (Fig.11) and 3 years 7 months post cementation (Fig.12).
Return to
Lower
Molar Immediate Implant, IBS,
Implant & Ortho
2
植牙,导板与正畸
Xin Wei, DDS, PhD, MS 1st edition 10/11/2016, last revision 01/04/2021